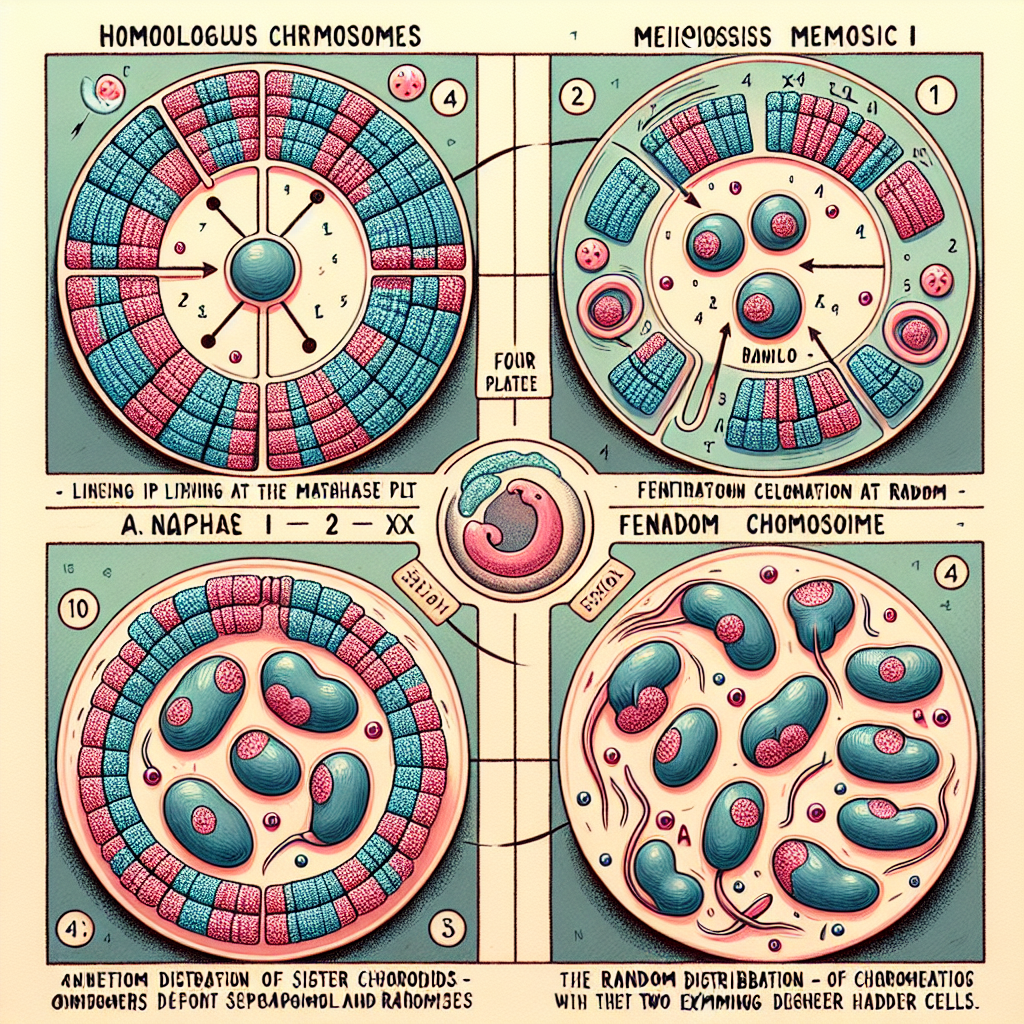
Independent assortment of chromosomes is a result of:
The random and independent way in which each pair of homologous chromosomes lines up at the metaphase plate during meiosis I
The random nature of fertilization of ova by sperm
The random distribution of the sister chromatids to the two daughter cells during anaphase II
The relatively small degree of homology shared by the X and Y chromosomes
All of the above are correct
The correct answer and explanation is :
The correct answer is:
The random and independent way in which each pair of homologous chromosomes lines up at the metaphase plate during meiosis I.
Explanation:
Independent assortment is one of the key mechanisms that contribute to genetic diversity during meiosis, and it refers to the random distribution of homologous chromosome pairs into gametes. This process occurs during metaphase I of meiosis.
- Meiosis I and the Metaphase Plate:
In meiosis, homologous chromosomes (chromosomes that carry the same types of genes but possibly different alleles) are paired. During metaphase I, these homologous pairs line up at the metaphase plate. The alignment of each pair is random, meaning that either chromosome from a pair can be placed on either side of the metaphase plate. This randomness results in a variety of possible combinations of chromosomes being distributed to the gametes, contributing to genetic variation. This phenomenon is known as independent assortment, as the inheritance of one pair of chromosomes is independent of the inheritance of another pair. - Other Options:
- Fertilization of ova by sperm: While fertilization is random in terms of which sperm will fertilize which egg, it does not directly result in independent assortment, as independent assortment occurs during meiosis in the formation of gametes.
- Distribution of sister chromatids during anaphase II: This refers to the separation of sister chromatids during meiosis II. While it is a critical step in ensuring each gamete gets the correct number of chromosomes, it does not directly contribute to independent assortment of homologous chromosomes, which is a feature of meiosis I.
- Homology of X and Y chromosomes: The X and Y chromosomes are not homologous in the typical sense because they carry different genetic information. Their relationship does not influence independent assortment directly in the context of chromosome pairs during meiosis I.
Thus, the key event leading to independent assortment is the random alignment of homologous chromosomes during metaphase I of meiosis, which ensures that chromosomes are assorted independently into gametes.