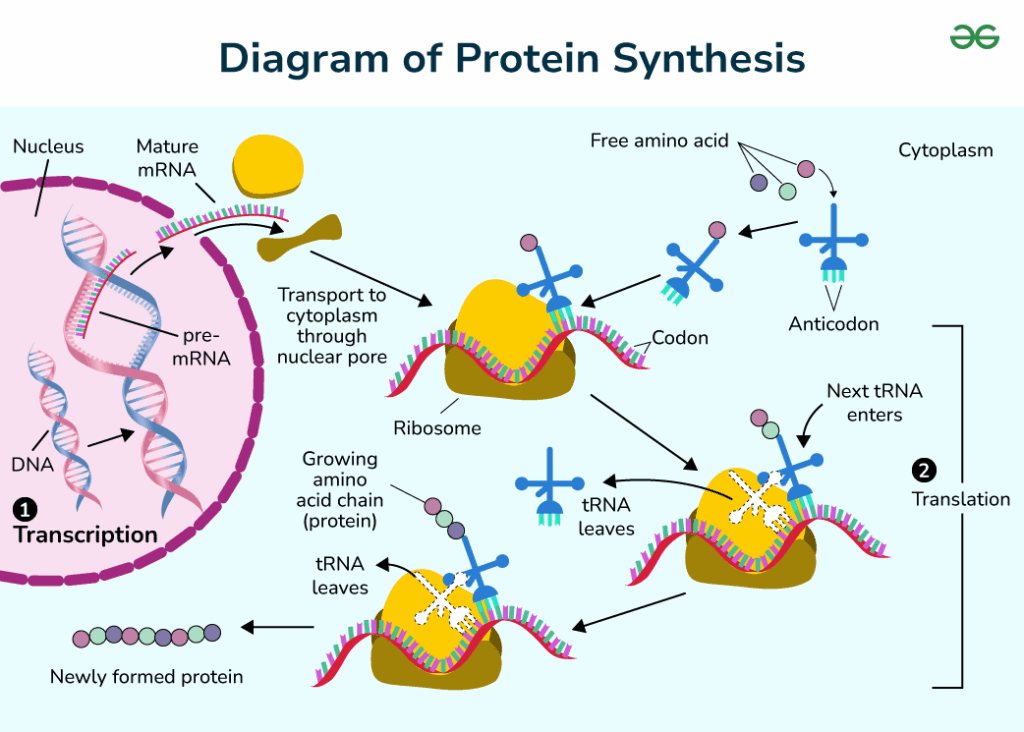
The process of protein synthesis involves two major stages: transcription and translation. These stages convert the genetic information in DNA into functional proteins, essential for cellular structure and function.
Name Class Date Guided Inquiry. Skills Lab Chapter 13 Lab From DNA To Protein Synthesis Problem What Are The Steps Involved In Making A Protein? Introduction Before A Protein Can Be Built, The Biochemical Blueprints For Its Construction Must Be Packaged And Transferred Out Of The DNA “Library.” First, The Specific Sequence Of DNA That Codes For The Protein
1. Transcription (DNA to mRNA)
Transcription occurs in the nucleus, where a segment of DNA is copied into messenger RNA (mRNA). The enzyme RNA polymerase binds to the DNA at a specific region called the promoter. It then unwinds the DNA strands and synthesizes a complementary strand of mRNA using the DNA template. This mRNA strand carries the genetic information from the DNA out of the nucleus to the cytoplasm. Before leaving the nucleus, the mRNA undergoes processing, including splicing to remove non-coding regions (introns), and the addition of a 5′ cap and a poly-A tail to protect the mRNA and aid in its export .
2. Translation (mRNA to Protein)
Once in the cytoplasm, the mRNA attaches to a ribosome, the cell’s protein synthesis machinery. The ribosome reads the mRNA in sets of three nucleotides, known as codons, each specifying an amino acid. Transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules, each carrying a specific amino acid, recognize these codons through their anticodons and bind to the mRNA. The ribosome facilitates the bonding of amino acids to form a polypeptide chain. This process occurs in three stages)
- Initiation: The ribosome assembles around the mRNA and the first tRNA.
- Elongation: Amino acids are added one by one to the growing polypeptide chain.
- Termination: The ribosome reaches a stop codon, releasing the completed protein .
This sequence of events—transcription followed by translation—is central to the central dogma of molecular biology: DNA → RNA → Protein. Proteins, composed of amino acid chains, perform a vast array of functions within living organisms, from catalyzing biochemical reactions to providing structural support to cells.
For a visual and detailed explanation, you might find this video helpful: