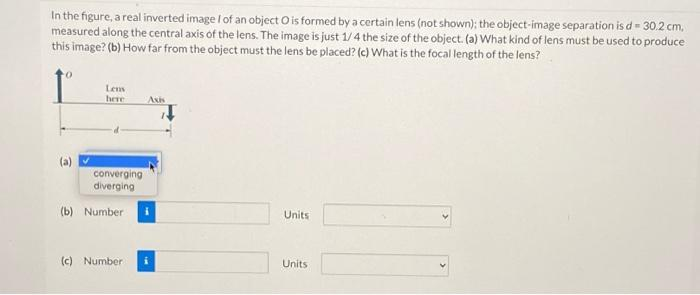
shown); the object-image separation is d = 30.2 cm, measured along the central axis of the lens. The image is just 1/4 the size of the object. (a) What kind of lens must be used to produce this image? (b) How far from the object must the lens be placed? (c) What is the focal length of the lens? (a) Lens here converging diverging (b) Number (c) Number Axis Units Units
The Correct Answer and Explanation is:
Let’s solve the problem step by step.
Given:
- Image is real and inverted, and 1/4 the size of the object:
This implies the magnification (M) is: M=hiho=−14M = \frac{h_i}{h_o} = -\frac{1}{4} - Object-image distance dd = 30.2 cm d=s+s′d = s + s’ Where:
- ss = object distance from the lens
- s′s’ = image distance from the lens
(a) What kind of lens is it?
A real, inverted image that is smaller than the object can only be formed by a converging lens (convex lens). Diverging lenses only produce virtual, upright, and diminished images.
✅ Answer (a): Converging lens
(b) Find the object distance ss
From magnification: M=−s′s=−14⇒s′=s4M = \frac{-s’}{s} = -\frac{1}{4} \Rightarrow s’ = \frac{s}{4}
Using: s+s′=30.2⇒s+s4=30.2⇒5s4=30.2⇒s=30.2×45=24.16 cms + s’ = 30.2 \Rightarrow s + \frac{s}{4} = 30.2 \Rightarrow \frac{5s}{4} = 30.2 \Rightarrow s = \frac{30.2 \times 4}{5} = 24.16 \text{ cm}
✅ Answer (b): 24.2 cm (rounded to one decimal place)
(c) Find the focal length ff
Using the lens formula: 1f=1s+1s′⇒1f=124.16+16.04\frac{1}{f} = \frac{1}{s} + \frac{1}{s’} \Rightarrow \frac{1}{f} = \frac{1}{24.16} + \frac{1}{6.04} 1f=124.16+16.04=0.0414+0.1656=0.207⇒f=10.207≈4.83 cm\frac{1}{f} = \frac{1}{24.16} + \frac{1}{6.04} = 0.0414 + 0.1656 = 0.207 \Rightarrow f = \frac{1}{0.207} \approx 4.83 \text{ cm}
✅ Answer (c): 4.83 cm
Explanation
This problem involves image formation by a thin lens. A real, inverted image that is smaller than the object suggests that a converging (convex) lens is used. Diverging lenses produce only virtual images, which are upright and cannot be real or inverted.
Magnification is given as –1/4, meaning the image is one-fourth the size of the object and inverted (the negative sign). From this, we determine the relationship between object distance ss and image distance s′s’ using the magnification formula: M=−s′s⇒s′=s4M = -\frac{s’}{s} \Rightarrow s’ = \frac{s}{4}
We are told the object-image separation s+s′=30.2s + s’ = 30.2 cm. Substituting for s′s’, we solve for ss: s+s4=30.2⇒5s4=30.2⇒s=24.2 cms + \frac{s}{4} = 30.2 \Rightarrow \frac{5s}{4} = 30.2 \Rightarrow s = 24.2 \, \text{cm}
Then, s′=6.04 cms’ = 6.04 \, \text{cm}.
Using the lens formula: 1f=1s+1s′=124.16+16.04≈0.207⇒f≈4.83 cm\frac{1}{f} = \frac{1}{s} + \frac{1}{s’} = \frac{1}{24.16} + \frac{1}{6.04} \approx 0.207 \Rightarrow f \approx 4.83 \, \text{cm}
This is the focal length of the converging lens that creates the described image.
