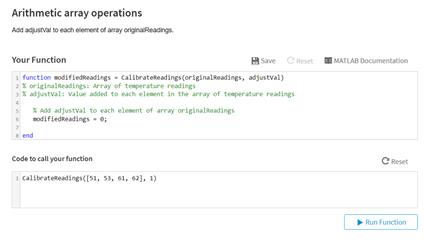
Arithmetic array operations
Add adjustVal to each element of array original Readings.
Your Function
- function modified Readings = Calibrate Readings(original Readings, adjustVal )
- % original Readings: Array of temperature readings
- % adjustVal : value added to each element in the array of temperature readings
4. - % Add adjustval to each element of array original Readings
- modified Readings = 0: end
7. - End
Code to call your function - Calibrate Readings ([51, 53, 61, 62], 1)
The Correct Answer and Explanation is:
Corrected MATLAB Function:
Here’s the corrected version of the MATLAB function based on your task:
function modifiedReadings = CalibrateReadings(originalReadings, adjustVal)
% originalReadings: Array of temperature readings
% adjustVal: Value added to each element in the array of temperature readings
% Add adjustVal to each element of array originalReadings
modifiedReadings = originalReadings + adjustVal;
end
Explanation
This MATLAB function CalibrateReadings is designed to adjust a series of temperature readings by adding a constant value (adjustVal) to each element in the array originalReadings. The main purpose is to calibrate or correct the data, such as when a thermometer consistently reads too low or too high and needs adjustment.
The original code has syntax and logical errors that prevent it from working correctly. Let’s go over the corrections:
- Function Header: The header must match MATLAB syntax, and variable names cannot include spaces. Therefore, change
modified ReadingstomodifiedReadings, andCalibrate ReadingstoCalibrateReadings. - Operation: The core operation in line 6,
modifiedReadings = 0;, was incorrect. This line simply setsmodifiedReadingsto 0, which does not apply the adjustment to each element of the input array. The correct operation ismodifiedReadings = originalReadings + adjustVal;. MATLAB allows element-wise operations on arrays, so adding a scalar (adjustVal) to a vector (originalReadings) results in a new vector where the scalar is added to each element. - Example: When the function is called as
CalibrateReadings([51, 53, 61, 62], 1), it returns[52, 54, 62, 63].
This simple function is a typical example of MATLAB’s strength in vectorized operations, which are concise, efficient, and avoid the need for explicit loops in many cases. Proper understanding and use of these operations are fundamental for efficient MATLAB programming, especially in data processing and numerical computing tasks.
