3(x+2)=3x+6 3x+2x=x^2(3+2) 3x+2=3(x+2) -3(2+x)=-6x-3
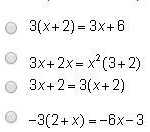
The Correct Answer and Explanation is:
The correct equation that shows the distributive property is:
3(x + 2) = 3x + 6
Explanation
The distributive property is a fundamental algebraic rule used to eliminate parentheses in expressions where a number is multiplied by a sum or difference. It states:
a(b + c) = ab + ac
This means that when a number or variable is placed outside a set of parentheses and multiplied by the sum inside, you multiply the outside number with each term inside individually, then add or subtract the results.
Let’s apply the distributive property to the correct option:
3(x + 2)
Using the distributive property:
- Multiply 3 by x → 3x
- Multiply 3 by 2 → 6
So:
3(x + 2) = 3x + 6
This matches the right-hand side of the equation in the first option:
3(x + 2) = 3x + 6
Let’s quickly examine the other choices:
- 3x + 2x = x²(3 + 2)
This is not using the distributive property. It involves an incorrect assumption about powers and addition. - 3x + 2 = 3(x + 2)
While this looks similar, it’s not a demonstration of the distributive property. Instead, it’s an equation you could solve, but not one that results directly from distribution. - –3(2 + x) = –6x – 3
Let’s distribute:
–3(2 + x) = –3×2 + (–3)×x = –6 – 3x
This is not equal to –6x – 3, so it is incorrect.
Summary:
Only the first equation (3(x + 2) = 3x + 6) correctly applies the distributive property. It demonstrates how a number multiplies across a sum inside parentheses to simplify an algebraic expression.
