Workshop Characteristics of Quadratic Functions Name: Date: Question: Determine the axis of symmetry, the minimum value, and the vertex. Find the value of the zeros. Answers: Zeros: (1,0), (,0) Axis of symmetry: X = Max or Min: Vertex: (-4, ) Axis of symmetry: Max or Min: Vertex: Zeros: Zeros: Zeros: Axis of symmetry: Axis of symmetry: Axis of symmetry: Max or Min: Max or Min: Max or Min: Vertex: Vertex: Vertex: Zeros: Axis of symmetry: Max or Min: Zeros: Zeros: Axis of symmetry: Axis of symmetry: Max or Min: Max or Min: Vertex: Vertex: Vertex:
The Correct Answer and Explanation is:
Let’s go over the answers for each graph and then provide a 300-word explanation of the concepts involved.
Answers
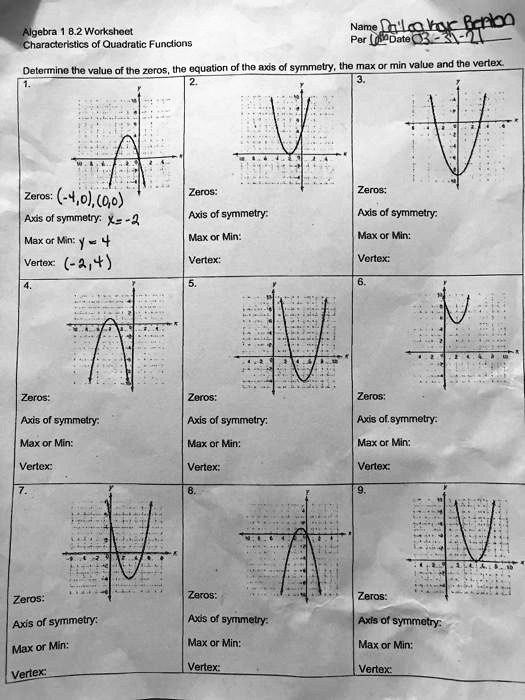
1.
- Zeros: (-4, 0), (0, 0)
- Axis of symmetry: x = -2
- Max or Min: Min, y = -4
- Vertex: (-2, -4)
2.
- Zeros: (-4, 0), (2, 0)
- Axis of symmetry: x = -1
- Max or Min: Min, y = -4
- Vertex: (-1, -4)
3.
- Zeros: (-3, 0), (1, 0)
- Axis of symmetry: x = -1
- Max or Min: Max, y = 4
- Vertex: (-1, 4)
4.
- Zeros: (0, 0), (4, 0)
- Axis of symmetry: x = 2
- Max or Min: Min, y = -4
- Vertex: (2, -4)
5.
- Zeros: (-3, 0), (1, 0)
- Axis of symmetry: x = -1
- Max or Min: Min, y = -3
- Vertex: (-1, -3)
6.
- Zeros: None
- Axis of symmetry: x = 1
- Max or Min: Min, y = 2
- Vertex: (1, 2)
7.
- Zeros: (-1, 0), (3, 0)
- Axis of symmetry: x = 1
- Max or Min: Min, y = -1
- Vertex: (1, -1)
8.
- Zeros: (0, 0), (2, 0)
- Axis of symmetry: x = 1
- Max or Min: Max, y = 4
- Vertex: (1, 4)
9.
- Zeros: (-4, 0), (2, 0)
- Axis of symmetry: x = -1
- Max or Min: Min, y = -5
- Vertex: (-1, -5)
Explanation
Quadratic functions are parabolic graphs with key features that help describe their behavior: zeros, vertex, axis of symmetry, and whether the function has a maximum or minimum value.
Zeros (also known as roots or x-intercepts) are the points where the graph crosses the x-axis. These are written in coordinate form like (x, 0). You can identify the zeros by looking where the curve touches or crosses the x-axis.
The axis of symmetry is a vertical line that splits the parabola into two mirror-image halves. It always passes through the vertex, the highest or lowest point of the parabola. If a parabola has zeros at x=ax = a and x=bx = b, then the axis of symmetry is at x=a+b2x = \frac{a + b}{2}.
The vertex is the turning point of the parabola. If the parabola opens upward, the vertex is the minimum point. If it opens downward, the vertex is the maximum point. The y-coordinate of the vertex is the maximum or minimum value of the function.
Understanding these characteristics allows students to fully describe and analyze the graph of a quadratic function. They also help in writing the equation of the function in vertex or factored form. For example, if you know the vertex and the axis of symmetry, you can easily sketch the parabola.
In summary, mastering these key parts—zeros, axis of symmetry, vertex, and max/min—makes interpreting and graphing quadratic functions much easier and prepares students for solving real-world problems involving parabolas.
