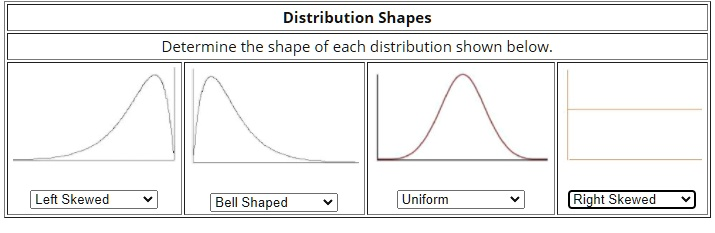
Distribution Shapes Determine the shape of each distribution shown below. Left Skewed Bell Shaped Uniform Right Skewed
The Correct Answer and Explanation is:
Correct Answers for Each Distribution Shape:
From left to right, the correct distribution shape labels are:
- Right Skewed
- Left Skewed
- Bell Shaped
- Uniform
Explanation
Understanding the shape of a distribution is critical in statistics, as it helps us describe data and choose the appropriate methods for analysis. Distributions can take on several forms, and four common types are shown in the image: skewed left, skewed right, bell-shaped (normal), and uniform.
The first graph displays a distribution with a long tail on the right side. This is known as right-skewed (or positively skewed). In such distributions, most of the data points cluster on the left, and fewer data points extend to the right. Examples include income distribution, where a few high earners stretch the graph to the right.
The second graph is the opposite—it has a long tail on the left side. This is left-skewed (or negatively skewed). Here, most values are concentrated on the right, with fewer lower values dragging the graph to the left. This pattern often appears in age-at-retirement data, where most people retire around the same age but a few retire very early.
The third graph shows a symmetric, bell-shaped curve. This is the classic bell-shaped distribution (or normal distribution). It is symmetric about the mean, with values tapering off equally on both sides. Many natural phenomena follow this pattern, including height, IQ scores, and measurement errors.
The fourth graph presents a flat, even distribution, indicating that all values occur with roughly equal frequency. This is known as a uniform distribution. It’s often used in simulations and modeling where each outcome is equally likely, like rolling a fair die.
Each distribution shape conveys different characteristics about data, including the presence of outliers, data spread, and central tendency, which are vital for proper statistical interpretation.
