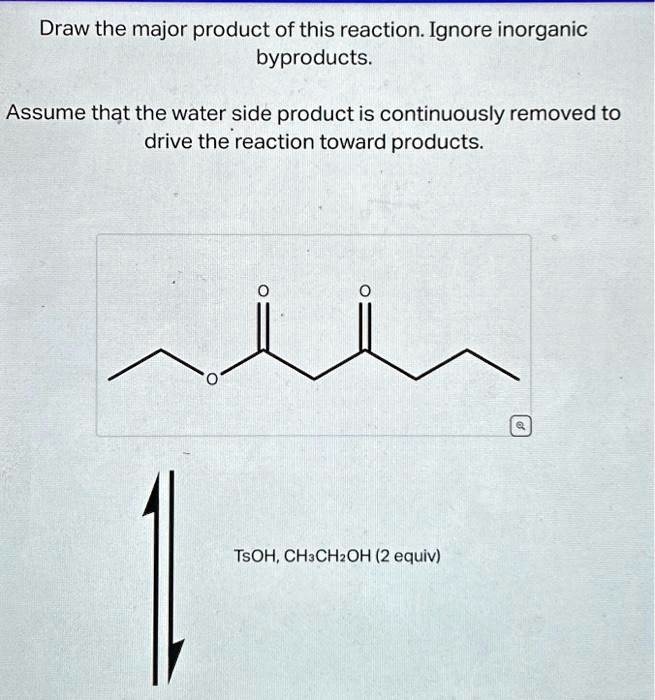
Draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Assume that the water side product is continuously removed to drive the reaction toward products. TSOH, CH
CH
OH (2 equiv)
The Correct Answer and Explanation is:
The starting compound shown is a 1,3,5-triketone with an ethyl ester on one end. The reaction conditions include:
- TsOH (p-toluenesulfonic acid): a strong organic acid catalyst.
- CH₃CH₂OH (ethanol), 2 equivalents.
- Removal of water, driving the equilibrium toward the product.
Reaction Overview:
This is a double acetal (or ketal) formation reaction. Acid-catalyzed ketone reaction with alcohols (especially in excess) forms acetals or ketals. In this molecule, there are two ketone groups and one ester group. Esters are less reactive under these conditions compared to ketones, so the two ketone groups are the reactive centers.
Mechanism and Product Formation:
- Ethanol (2 equiv) reacts with each ketone group.
- In the presence of acid catalyst (TsOH), each ketone undergoes nucleophilic attack by ethanol, followed by proton transfers and loss of water.
- Since water is removed, the equilibrium favors acetal formation.
- Each ketone is converted into a diethexy acetal:
- –C=O → –C(OC₂H₅)₂
Final Product:
The major product is a molecule where the two ketone groups have each been converted to acetals (diethexy). The ester functional group remains unchanged.
Structural Summary of the Major Product:
- A 7-carbon chain with:
- C2: acetal (C bonded to two ethoxy groups)
- C4: ester group (unchanged)
- C6: acetal (C bonded to two ethoxy groups)
Conclusion (Summary):
This is an acid-catalyzed acetal formation reaction. The major product is formed by reaction of the two ketones with 2 equivalents of ethanol, forming two acetal groups. The removal of water ensures the equilibrium favors product formation. The ester group does not react under these conditions.
