PLANT CELL ANIMAL CELL J I H G F E D C B A
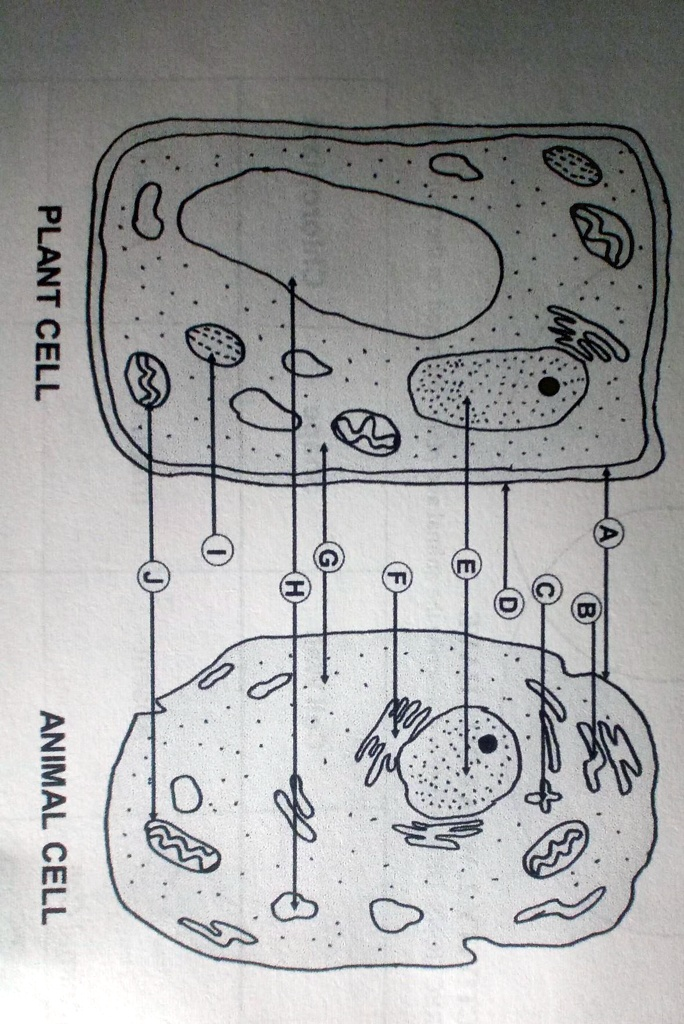
Labelled Cell Structures:
Here are the correct names of the labelled parts in the plant and animal cell diagram:
A – Cell membrane
B – Cytoplasm
C – Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER)
D – Nucleus
E – Nucleolus
F – Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER)
G – Vacuole
H – Ribosome
I – Chloroplast (only in plant cell)
J – Cell Wall (only in plant cell)
K – Mitochondria (unlabelled but visible)
Explanation (300 Words Approx.):
Cells are the basic structural and functional units of life. They are mainly classified into two types: plant cells and animal cells. Although they share several common organelles, there are distinct differences in their structures and functions.
Both plant and animal cells possess a cell membrane (A) that encloses the cell, controlling the movement of substances in and out. Inside the membrane lies the cytoplasm (B), a jelly-like substance that holds various organelles.
The endoplasmic reticulum (C & F) is of two types: rough (with ribosomes) and smooth (without ribosomes). The rough ER (C) aids in protein synthesis, while the smooth ER (F) is involved in lipid synthesis and detoxification.
The nucleus (D) serves as the control center of the cell, containing genetic material (DNA). Within it lies the nucleolus (E), which produces ribosomes. Ribosomes (H) are small structures that synthesize proteins.
Mitochondria (K), known as the powerhouses of the cell, are involved in energy production through cellular respiration. They are present in both plant and animal cells.
However, some structures are unique to plant cells. The cell wall (J) provides structural support and protection. The large central vacuole (G) helps maintain cell rigidity and stores nutrients and waste products. Chloroplasts (I) contain chlorophyll and are responsible for photosynthesis, a process by which plants convert sunlight into chemical energy.
Animal cells lack chloroplasts and a rigid cell wall. Their vacuoles are smaller and more numerous compared to the large central vacuole in plant cells.
Understanding these cell organelles and their functions is fundamental in biology as they play critical roles in the life processes of organisms.
