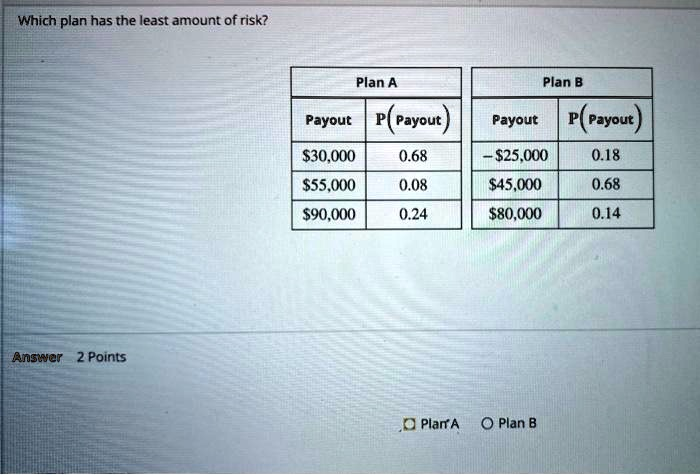
Which plan has the least amount of risk? Plan A Plan B Payout P (Payout) Payout P (Payout)
55,000
25,000
80,000 0.18 0.68 0.14 0.08 0.24 Answer: 2 Points Plan A Plan B
The Correct Answer and Explanation is:
Correct Answer: Plan A
Explanation
In financial analysis and probability theory, risk is a measure of the uncertainty or variability of potential outcomes for an investment. A common and robust method for quantifying this risk is by calculating the standard deviation of the probability distribution of payouts. The standard deviation measures how much the individual outcomes are dispersed or spread out from the average outcome (the expected value). A lower standard deviation indicates that the potential outcomes are clustered more closely around the expected value, implying less volatility and therefore, less risk. Conversely, a higher standard deviation signifies greater variability and higher risk.
To determine which plan has the least amount of risk, we must calculate the standard deviation for both Plan A and Plan B.
1. Calculation for Plan A:
- Expected Value (E[A]): The weighted average of the payouts.
E[A] = (30,000×0.68)+(30,000×0.68)+(55,000 × 0.08) + ($90,000 × 0.24)
E[A] = $20,400 + $4,400 +21,600=∗∗21,600=∗∗46,400** - Variance (σ²[A]): The weighted average of the squared differences from the Expected Value.
σ²[A] = (30,000 – 46,400)²(0.68) + (55,000 – 46,400)²(0.08) + (90,000 – 46,400)²(0.24)
σ²[A] = (-16,400)²(0.68) + (8,600)²(0.08) + (43,600)²(0.24)
σ²[A] = 182,892,800 + 5,916,800 + 456,230,400 = 645,040,000 - Standard Deviation (σ[A]): The square root of the variance.
σ[A] = √645,040,000 ≈ $25,397.64
2. Calculation for Plan B:
- Expected Value (E[B]):
E[B] = (-25,000×0.18)+(25,000×0.18)+(45,000 × 0.68) + (80,000×0.14)E[B]=−80,000×0.14)E[B]=−4,500 + $30,600 +11,200=∗∗11,200=∗∗37,300** - Variance (σ²[B]):
σ²[B] = (-25,000 – 37,300)²(0.18) + (45,000 – 37,300)²(0.68) + (80,000 – 37,300)²(0.14)
σ²[B] = (-62,300)²(0.18) + (7,700)²(0.68) + (42,700)²(0.14)
σ²[B] = 698,632,200 + 40,317,200 + 255,260,600 = 994,210,000 - Standard Deviation (σ[B]):
σ[B] = √994,210,000 ≈ $31,531.10
Conclusion:
Comparing the standard deviations, Plan A (σ ≈ $25,398) has a significantly lower standard deviation than Plan B (σ ≈
31,531).ThisindicatesthatthepotentialpayoutsforPlanAarelessspreadoutandmorepredictablethanthoseforPlanB.Furthermore,PlanBincludesthepossibilityofasignificantloss(−31,531).ThisindicatesthatthepotentialpayoutsforPlanAarelessspreadoutandmorepredictablethanthoseforPlanB.Furthermore,PlanBincludesthepossibilityofasignificantloss(−25,000), which inherently represents a higher level of risk compared to Plan A, where all possible outcomes are positive gains. Therefore, based on the quantitative measure of standard deviation, Plan A has the least amount of risk.thumb_upthumb_down
