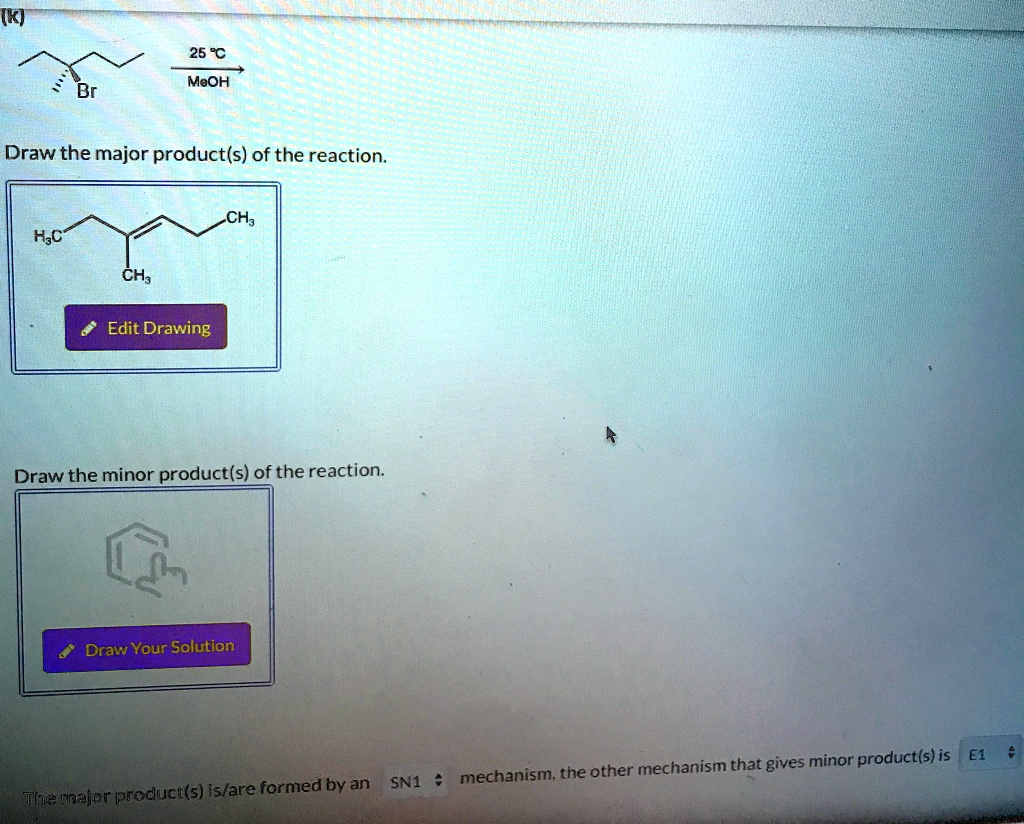
25 °C MeOH Br Draw the major product(s) of the reaction. CH
H
C CH
Edit Drawing Draw the minor product(s) of the reaction. Draw Your Solution The major product(s) is/are formed by an SN1 mechanism, the other mechanism that gives minor product(s) is E1
The Correct Answer and Explanation is:
Based on the provided reaction, here is the complete and correct solution.
Analysis of the Reaction:
- Substrate: The starting material is (3R)-3-bromo-3-methylhexane. The bromine atom is attached to a tertiary carbon, which is sterically hindered for SN2 reactions but readily forms a stable tertiary carbocation.
- Reagent/Solvent: Methanol (MeOH) is a weak nucleophile and a weak base. It is also a polar protic solvent, which stabilizes the carbocation intermediate necessary for SN1 and E1 reactions.
- Conditions: The reaction is run at 25 °C, which is a relatively low temperature. Elimination reactions (E1) are favored by heat, while substitution reactions (SN1) are favored at lower temperatures.
Conclusion on Mechanism:
Given the tertiary substrate, weak nucleophile/base, and low temperature, the reaction will proceed via a competition between SN1 and E1 mechanisms. The SN1 pathway will be favored, producing the major product(s), while the E1 pathway will be the minor pathway.
Corrected Solution:
Draw the major product(s) of the reaction.
The major product is formed via an SN1 mechanism. The reaction proceeds through a planar tertiary carbocation intermediate, which loses its original stereochemistry. The nucleophile, methanol, can then attack from either face of the carbocation, resulting in a racemic mixture of the substitution product.
- Major Product: 3-methoxy-3-methylhexane (racemic mixture)
Draw the minor product(s) of the reaction.
The minor products are formed via an E1 mechanism. The weak base (methanol) removes a proton from a carbon adjacent (β-carbon) to the carbocation. There are two different types of β-hydrogens (on C2 and C4), leading to two constitutional isomers. According to Zaitsev’s rule, the more substituted alkene is favored. In this case, both possible alkenes are trisubstituted, so a mixture of both is expected.
- Minor Products: 3-methylhex-3-ene and 3-methylhex-2-ene
Complete the statement below:
The major product(s) is/are formed by an SN1 mechanism, the other mechanism that gives minor product(s) is E1.thumb_upthumb_down
