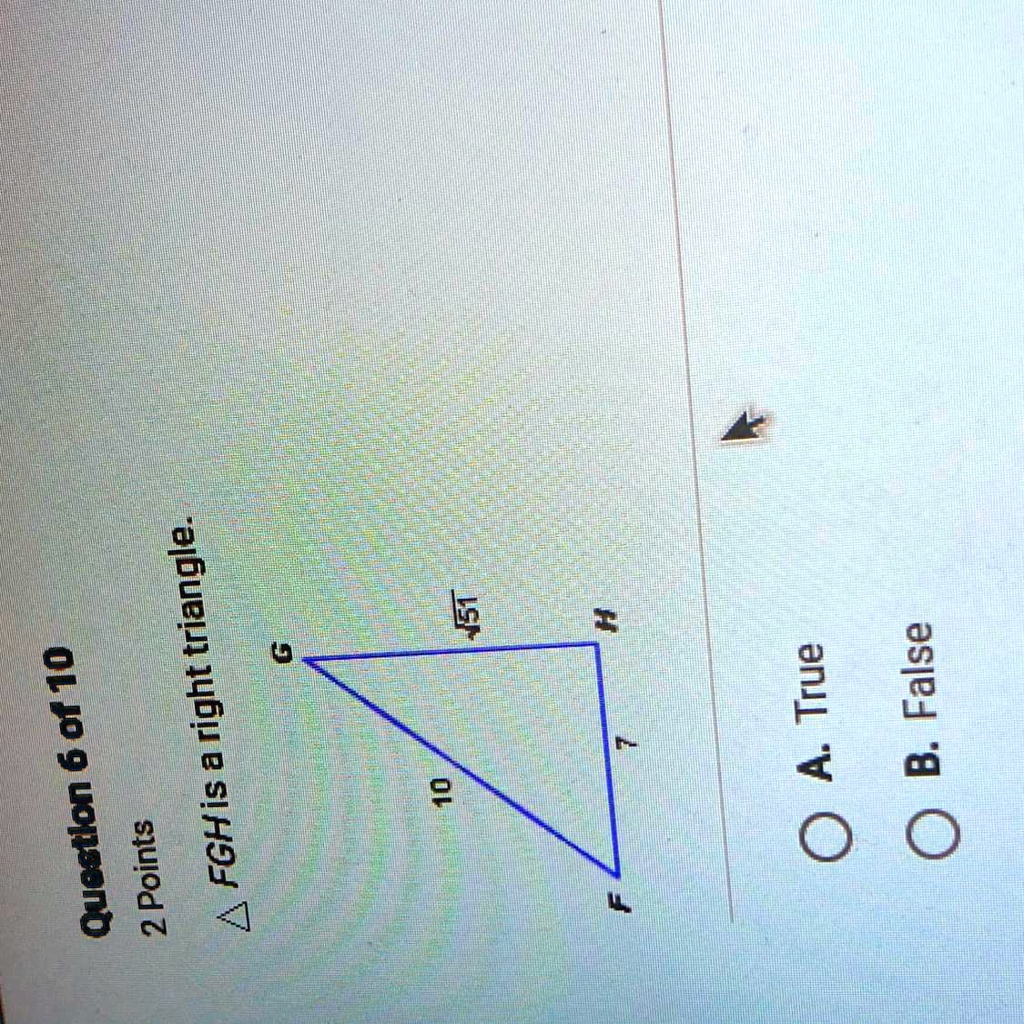
Triangle FGH is a right triangle.
The Correct Answer and Explanation is:
A. True
To determine if ΔFGH is a right triangle, the converse of the Pythagorean theorem must be applied. This theorem states that if a triangle’s side lengths satisfy the equation a² + b² = c², where ‘c’ is the length of the longest side, then the triangle is a right triangle.
First, let’s identify the lengths of the three sides of the triangle from the image:
- Side FH has a length of 7.
- Side GH has a length of √51.
- Side FG has a length of 10.
The longest side of the triangle is FG, with a length of 10. If this is a right triangle, FG must be the hypotenuse. The other two sides, FH and GH, would be the legs.
Next, substitute these lengths into the Pythagorean formula (a² + b² = c²):
(FH)² + (GH)² = (FG)²
7² + (√51)² = 10²
Now, calculate the square of each value:
- 7² equals 7 × 7, which is 49.
- (√51)² equals 51, as squaring a square root cancels it out.
- 10² equals 10 × 10, which is 100.
Let’s check if the equation is balanced with these calculated values:
49 + 51 = 100
100 = 100
The sum of the squares of the two shorter sides (49 + 51) is exactly equal to the square of the longest side (100). Because this relationship holds true, the triangle satisfies the conditions of the converse of the Pythagorean theorem. Therefore, the statement that ΔFGH is a right triangle is correct. The right angle is at vertex H, which is opposite the longest side (the hypotenuse FG).
