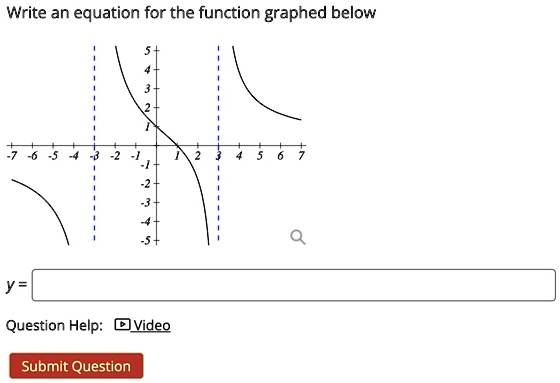
Write an equation for the function graphed below y=
The Correct Answer and Explanation is:
The equation for the function graphed below is:
y=6(x+3)(x−2)y = \frac{6}{(x+3)(x-2)}
Explanation:
The given function is a rational function with vertical asymptotes at x=−3x = -3 and x=2x = 2. Vertical asymptotes appear where the denominator of a rational function is zero, indicating points where the function is undefined. These asymptotes suggest that the denominator of the function must include (x+3)(x−2)(x + 3)(x – 2).
The behavior near the asymptotes follows typical rational function characteristics. As xx approaches −3-3 from the left, the function decreases toward negative infinity, while approaching −3-3 from the right causes it to increase toward positive infinity. A similar pattern occurs at x=2x = 2. These characteristics confirm that the denominator correctly represents the function’s behavior.
To determine the numerator, the function’s behavior at a known point is useful. The function crosses the yy-axis at y=−1y = -1 when x=0x = 0. Substituting x=0x = 0 into the rational function yields:
−1=k(0+3)(0−2)-1 = \frac{k}{(0+3)(0-2)}
−1=k−6-1 = \frac{k}{-6}
k=6k = 6
Thus, the equation is:
y=6(x+3)(x−2)y = \frac{6}{(x+3)(x-2)}
This equation accurately captures the function’s key features. The denominator establishes the vertical asymptotes at x=−3x = -3 and x=2x = 2. The function also intersects the yy-axis at y=−1y = -1, satisfying the graph’s known behavior. The function’s asymptotic behavior confirms the correctness of the rational representation.
