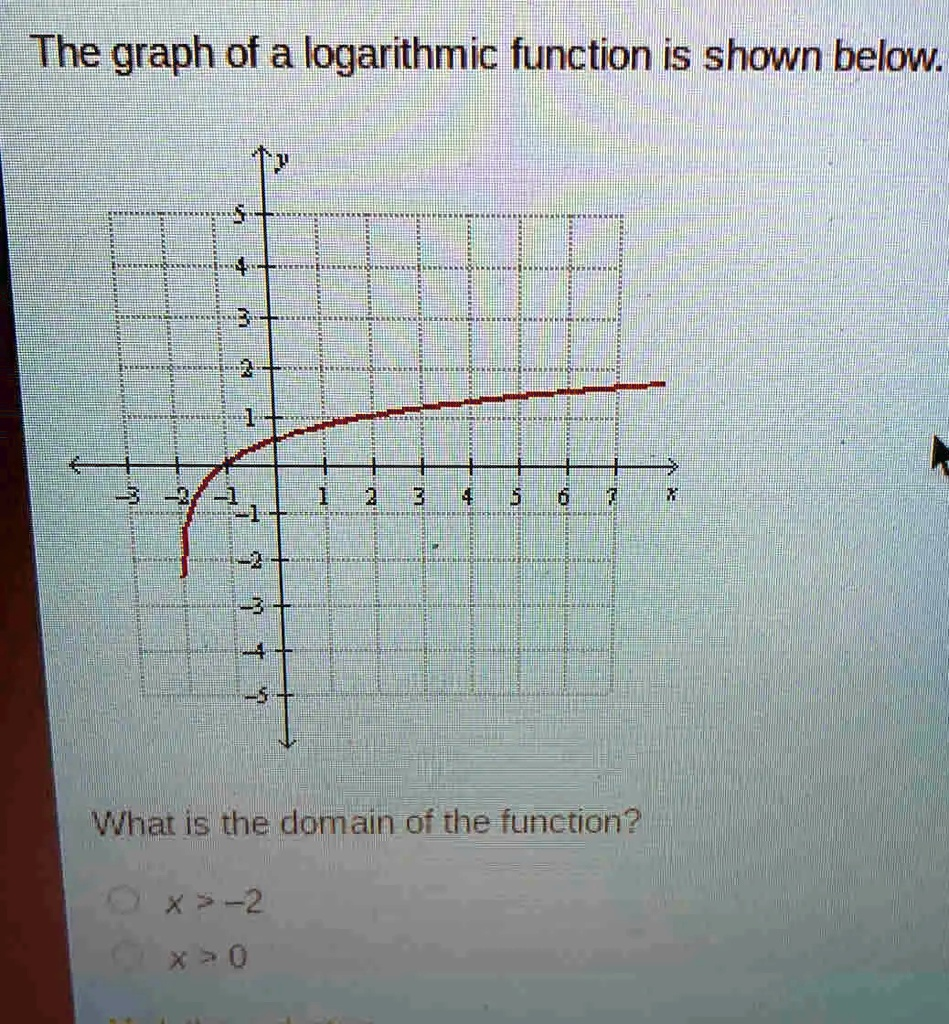
The graph of a logarithmic function is shown below. What is the domain of the function? x > -2 x > 0
The Correct Answer and Explanation is:
The correct answer is x > -2.
Explanation:
The domain of a logarithmic function is determined by the values for which the argument inside the logarithm is positive. Since logarithmic functions are undefined for negative numbers and zero, we must consider the point where the function begins to be defined.
From the given graph, the logarithmic function passes through x = -2, indicating that this is the boundary where the function becomes valid. This means the function is defined for all values greater than -2. Logarithmic functions generally have a vertical asymptote, which represents a value of x that the function approaches but never crosses. In this case, the asymptote occurs at x = -2, making it the lowest value that x can take without making the function undefined.
Comparing the two given options, x > 0 would incorrectly exclude part of the function’s domain. Since the function is defined for values greater than -2, selecting x > 0 would only represent part of the valid domain instead of the entire range.
Understanding logarithmic functions requires recognizing that they are restricted by their argument. The argument inside the logarithm must remain positive for the function to be valid. When analyzing the graph, the key step is identifying the lowest value at which the function is valid, which in this case is -2. The function then continues indefinitely for larger values of x, growing at a slower rate.
Thus, the correct domain is x > -2, reflecting all valid input values for the function without restricting it unnecessarily.
