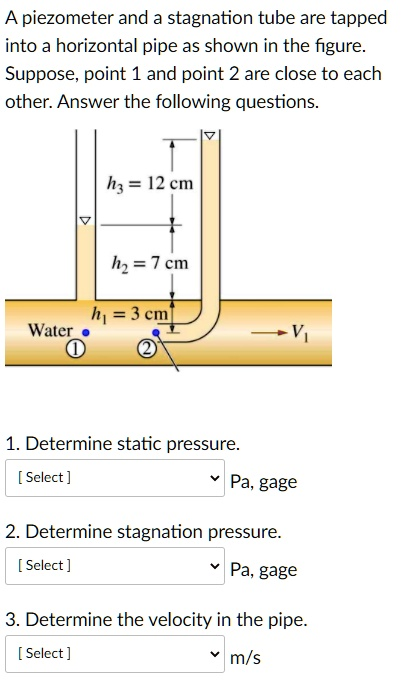
A piezometer and a stagnation tube are tapped into a horizontal pipe as shown in the figure. Suppose, point 1 and point 2 are close to each other. Answer the following questions.
Water 1 2 1. Determine static pressure. [Select] Pa, gage 2. Determine stagnation pressure. [Select] Pa, gage 3. Determine the velocity in the pipe. [Select] m/s
The Correct Answer and Explanation is:
Here is a step-by-step solution to the problem.
Given Information:
- Fluid: Water (density, ρ ≈ 1000 kg/m ³)
- Acceleration due to gravity, g ≈ 9.81 m/s²
- Height in piezometer above the pipe centerline, h₂ = 7 cm = 0.07 m
- Difference in height between stagnation tube and piezometer, h₃ = 12 cm = 0.12 m
1. Determine static pressure.
The static pressure in the pipe is measured by the piezometer. The height of the water column in the piezometer (h₂) corresponds to the static pressure head. The gage pressure is calculated using the gage) is calculated using the total height:P = ρ * g * h_total`
- Given values:
- ρ = 1000 kg/m ³
- g = 9.81 m/s²
- Total height (h₂ + h₃) = 7 cm + 12 cm = 19 cm = 0.19 m
- Calculation:
P_stagnation, gage = 1000 kg/m³ * 9.81 m/s² * 0.19 m
`P_stagn hydrostatic pressure formula:
P_static = ρ * g * h₂
Calculation:
P_static = (1000 kg/m ³) * (9.81 m/s²) * (0.07 m)
P_static = 686.7 Pa
Answer: The static pressure is 686.7 Pa, gage.
2. Determine stagnation pressure.
The stagnation pressure is measured by the stagnation tube (also known as a Pitot tube). The total height of the water column in this tube corresponds to the stagnation pressure head. From the diagram, this height is the sum of h₂ and h₃.
Stagnation head, h_stagnation = h₂ + h₃
h_stagnation = 7 cm + 1ation, gage = 1863.9 Pa`
The stagnation pressure is 1863.9 Pa, gage.
3. Determine the velocity in the pipe.
The velocity of the fluid (V₁) can be determined using Bernoulli’s equation between point 1 (free stream) and point 2 (stagnation point). The difference between the stagnation pressure and static pressure is the dynamic pressure, which is related to the fluid’s velocity.
- Formula: The velocity can be found directly from the dynamic pressure head, which is h₃. The formula is V = sqrt(2 * g * h₃).
- Given values:
- g = 9.81 m/s²
- Dynamic pressure head (h₃) = 12 cm = 0.12 m
- Calculation:
V₁ = sqrt(2 * 9.81 m/s² * 0.12 m)
V₁ = sqrt(2.3544) m/s
V₁ ≈ 1.53 m/s
**The velocity in the pipe is 1.53 m/s.**2 cm = 19 cm = 0.19 m
The gage stagnation pressure is:
P_stagnation = ρ * g * h_stagnation
Calculation:
P_stagnation = (1000 kg/m ³) * (9.81 m/s²) * (0.19 m)
P_stagnation = 1863.9 Pa
Answer: The stagnation pressure
Summary of Answers:
- Determine static pressure.
[686.7] Pa, gage - Determine stagnation pressure.
[1863.9] Pa, gage - Determine the velocity in the pipe.
[1.53] is 1863.9 Pa, gage.
3. Determine the velocity in the pipe.
The velocity of the fluid (V) can be found using Bernoulli’s principle. The difference between the stagnation pressure and the static pressure is the dynamic pressure, which is related to the fluid’s velocity.
P_stagnation = P_static + m/s (1/2) * ρ * V²
Alternatively, we can use the pressure heads. The difference in the water levels between the stagnation tube and the piezometer (h₃) represents the dynamic head.
Dynamic head = V
