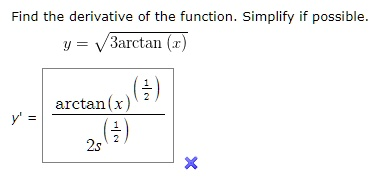
Find the derivative of the function: Simplify if possible – 3arctan(arctan)
The Correct Answer and Explanation is:
Of course. Here is the correct answer and a detailed explanation.
Correct Answer:
The derivative of the function y = sqrt(3*arctan(x)) is:
y’ = 3 / (2(1 + x^2) * sqrt(3*arctan(x)))
Explanation:
To find the derivative of the function y = sqrt(3*arctan(x)), we need to use the Chain Rule. The Chain Rule is used for differentiating composite functions, which are functions nested inside other functions.
1. Rewrite the Function
First, it is helpful to rewrite the square root as a fractional exponent. This makes applying the power rule more straightforward.
y = (3*arctan(x))^(1/2)
2. Identify the Inner and Outer Functions
The function is a composition of two parts:
- The outer function is the square root part, which we can call f(u) = u^(1/2).
- The inner function is the part inside the square root, which we can call g(x) = 3*arctan(x).
3. Apply the Chain Rule
The Chain Rule states that the derivative of a composite function y = f(g(x)) is the derivative of the outer function with respect to the inner function, multiplied by the derivative of the inner function. The formula is:
y’ = f'(g(x)) * g'(x)
4. Find the Derivatives of the Parts
- Derivative of the outer function: We use the power rule to differentiate f(u) = u^(1/2).
f'(u) = (1/2) * u^(1/2 – 1) = (1/2) * u^(-1/2) = 1 / (2 * u^(1/2)) - Derivative of the inner function: We differentiate g(x) = 3*arctan(x). The derivative of arctan(x) is a standard result: 1 / (1 + x^2).
g'(x) = 3 * d/dx(arctan(x)) = 3 * (1 / (1 + x^2)) = 3 / (1 + x^2)
5. Combine and Simplify
Now, we substitute these pieces back into the Chain Rule formula:
y’ = [1 / (2 * (3*arctan(x))^(1/2))] * [3 / (1 + x^2)]
Multiplying the numerators and denominators gives us the final simplified answer:
y’ = 3 / (2 * (1 + x^2) * sqrt(3*arctan(x)))
