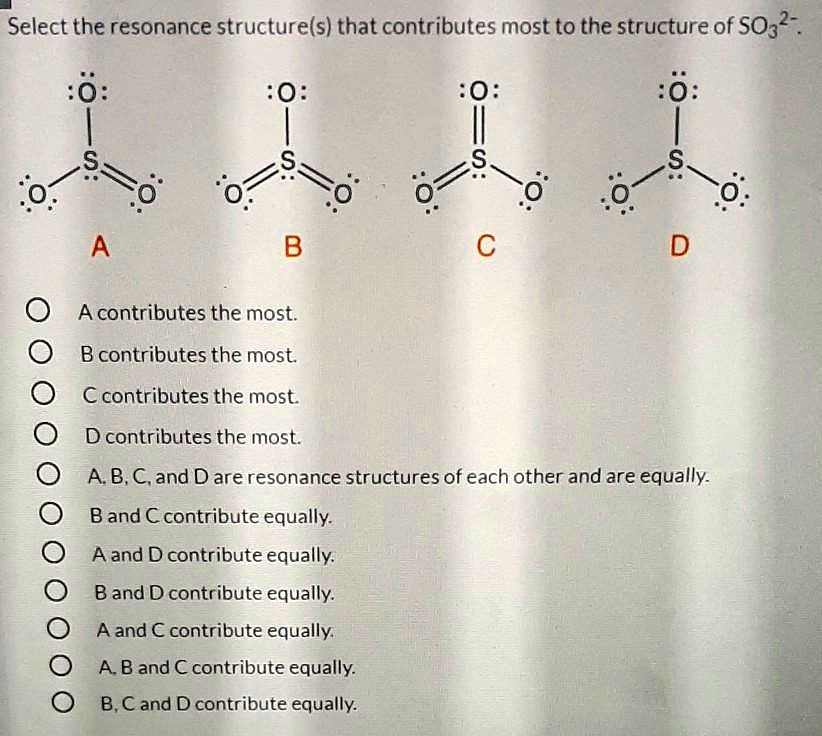
Select the resonance structure(s) that contributes most to the structure of SO32- S {0 A 0; C D 0 A contributes the most B contributes the most 0 C contributes the most D contributes the most. A, B, C, and D are resonance structures of each other and contribute equally. B and C contribute equally. A and D contribute equally. A and € contribute equally. A, B, and C contribute equally. B, C, and D contribute equally.
The Correct Answer and Explanation is:
The correct answer is A, B, and C contribute equally.
Here is an explanation of why this is the correct choice:
To determine which resonance structure contributes most to the overall structure of an ion, we need to find the most stable structure(s). The stability of a resonance structure is primarily determined by its formal charges. The most stable structures are those that:
- Have the fewest atoms with non-zero formal charges.
- Place any negative formal charges on the most electronegative atoms and any positive formal charges on the least electronegative atoms.
Let’s calculate the formal charges for each atom in the given structures. The formula for formal charge is:
Formal Charge = (Valence Electrons) – (Non-bonding Electrons) – (1/2 * Bonding Electrons)
Sulfur (S) has 6 valence electrons, and Oxygen (O) has 6 valence electrons.
Analysis of Structures A, B, and C:
These three structures are equivalent, just with the double bond in a different position. Let’s analyze structure A as a representative example:
- Sulfur (S): It has 1 lone pair (2 non-bonding electrons) and 4 bonds (8 bonding electrons).
Formal Charge (S) = 6 – 2 – (1/2 * 8) = 0 - Doubly-bonded Oxygen (O=): It has 2 lone pairs (4 non-bonding electrons) and 2 bonds (4 bonding electrons).
Formal Charge (O=) = 6 – 4 – (1/2 * 4) = 0 - Singly-bonded Oxygens (O-): Each has 3 lone pairs (6 non-bonding electrons) and 1 bond (2 bonding electrons).
Formal Charge (O-) = 6 – 6 – (1/2 * 2) = -1
The total charge for structures A, B, and C is 0 (S) + 0 (O=) + (-1) (O-) + (-1) (O-) = -2.
Analysis of Structure D:
- Sulfur (S): It has 1 lone pair (2 non-bonding electrons) and 3 bonds (6 bonding electrons).
Formal Charge (S) = 6 – 2 – (1/2 * 6) = +1 - Singly-bonded Oxygens (O-): Each of the three oxygens has 3 lone pairs (6 non-bonding electrons) and 1 bond (2 bonding electrons).
Formal Charge (O-) = 6 – 6 – (1/2 * 2) = -1
The total charge for structure D is +1 (S) + 3*(-1) (O) = -2.
Conclusion:
Structures A, B, and C have formal charges of 0, 0, -1, and -1. Structure D has formal charges of +1, -1, -1, and -1. According to the rules of stability, structures A, B, and C are more stable and therefore contribute more to the overall resonance hybrid because they have more atoms with a formal charge of zero and avoid placing a positive formal charge on the sulfur atom.
Since structures A, B, and C are chemically equivalent (only differing in the location of the double bond), they are equally stable and contribute equally to the true structure of the sulfite ion. Therefore, A, B, and C are the major resonance contributors.
