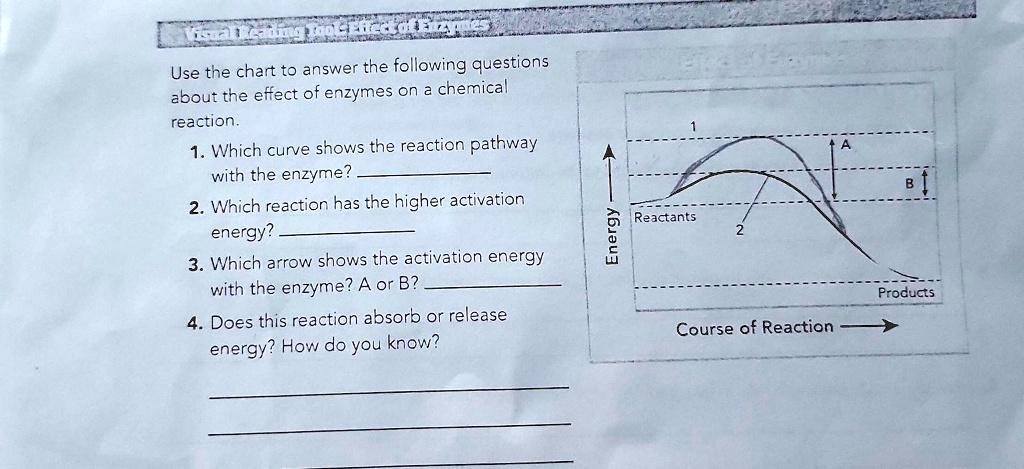
Use the chart to answer the following questions about the effect of enzymes on a chemical reaction. 1. Which curve shows the reaction pathway with the enzyme? 2. Which reaction has the higher activation energy? 3. Which arrow shows the activation energy with the enzyme? A or B? 4. Does this reaction absorb or release energy? How do you know? Energy 1 A B Reactants 2 Products Course of Reaction
The Correct Answer and Explanation is:
Here are the answers to the questions based on the provided chart.
- Curve 2
- The reaction shown by curve 1
- B
- This reaction releases energy. You know this because the energy level of the products is lower than the energy level of the reactants.
Explanation
This graph illustrates the energy changes that occur during a chemical reaction. The vertical axis represents the amount of potential energy, while the horizontal axis represents the progress of the reaction over time.
Enzymes are biological catalysts that accelerate chemical reactions by providing an alternative reaction pathway with a lower activation energy. Activation energy is the minimum amount of energy required to start a reaction, represented by the “hump” on the graph.
For question one, we must identify the enzyme-catalyzed reaction. Since enzymes lower the activation energy, the reaction with the enzyme will have the smaller energy hump. Curve 2 clearly shows a lower peak than curve 1, so it represents the reaction pathway with the enzyme.
For question two, the reaction with the higher activation energy is the one without the enzyme. This corresponds to the larger energy hump, which is depicted by curve 1. This uncatalyzed reaction requires a much greater input of energy to proceed.
For question three, we identify the arrow corresponding to the activation energy of the catalyzed reaction. As established, curve 2 is the pathway with the enzyme. Arrow B measures the energy from the reactants to the peak of curve 2. Therefore, B represents the activation energy with the enzyme present. Arrow A represents the higher activation energy for the uncatalyzed reaction.
Finally, for question four, we determine if the reaction is releasing or absorbing energy. This is found by comparing the starting energy of the reactants to the final energy of the products. On the graph, the products are at a lower energy level than the reactants. This difference in energy was released into the surroundings during the reaction. Such a reaction is known as an exothermic or exergonic reaction. If the products had a higher energy level than the reactants, it would be an endothermic reaction that absorbs energy.
