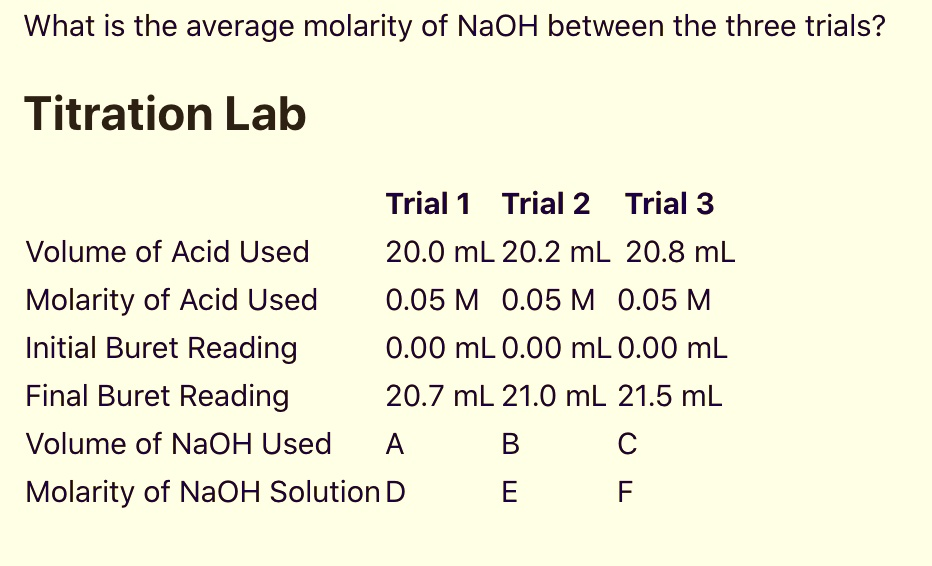
What is the average molarity of NaOH between the three trials? Titration Lab Trial 1 Trial 2 Trial 3 20.0 mL 20.2 mL 20.8 mL 0.05 M 0.05 M 0.05 M 0.00 mL O.00 mL 0.00 mL 20.7 mL 21.0 mL 21.5 mL Volume of Acid Used Molarity of Acid Used Initial Buret Reading Final Buret Reading Volume of NaOH Used Molarity of NaOH Solution D
The Correct Answer and Explanation is:
To find the average molarity of NaOH across the three trials, we first need to determine the volume of NaOH used in each trial and then calculate the molarity for each trial.
- Volume of NaOH Used:
- For each trial, the volume of NaOH used is the difference between the final and initial buret readings.
- Trial 1: Final Buret Reading = 20.7 mL, Initial Buret Reading = 0.0 mL
Volume of NaOH Used = 20.7 mL – 0.0 mL = 20.7 mL - Trial 2: Final Buret Reading = 21.0 mL, Initial Buret Reading = 0.0 mL
Volume of NaOH Used = 21.0 mL – 0.0 mL = 21.0 mL - Trial 3: Final Buret Reading = 21.5 mL, Initial Buret Reading = 0.0 mL
Volume of NaOH Used = 21.5 mL – 0.0 mL = 21.5 mL
- Molarity of NaOH:
To calculate the molarity of NaOH in each trial, we can use the titration equation: M1V1=M2V2M_1 V_1 = M_2 V_2M1V1=M2V2 where:- M1M_1M1 = Molarity of acid (0.05 M for all trials)
- V1V_1V1 = Volume of acid (given in the table)
- M2M_2M2 = Molarity of NaOH (what we are solving for)
- V2V_2V2 = Volume of NaOH used (calculated above)
- Trial 1:
- Volume of Acid Used = 20.0 mL, Molarity of Acid Used = 0.05 M, Volume of NaOH Used = 20.7 mL
- Trial 2:
- Volume of Acid Used = 20.2 mL, Molarity of Acid Used = 0.05 M, Volume of NaOH Used = 21.0 mL
- Trial 3:
- Volume of Acid Used = 20.8 mL, Molarity of Acid Used = 0.05 M, Volume of NaOH Used = 21.5 mL
- Average Molarity:
Now, to find the average molarity of NaOH, we add the molarities from each trial and divide by 3: Average Molarity=0.0483+0.0483+0.04843=0.0483 M\text{Average Molarity} = \frac{0.0483 + 0.0483 + 0.0484}{3} = 0.0483 \, \text{M}Average Molarity=30.0483+0.0483+0.0484=0.0483M
Thus, the average molarity of NaOH across the three trials is 0.0483 M.
