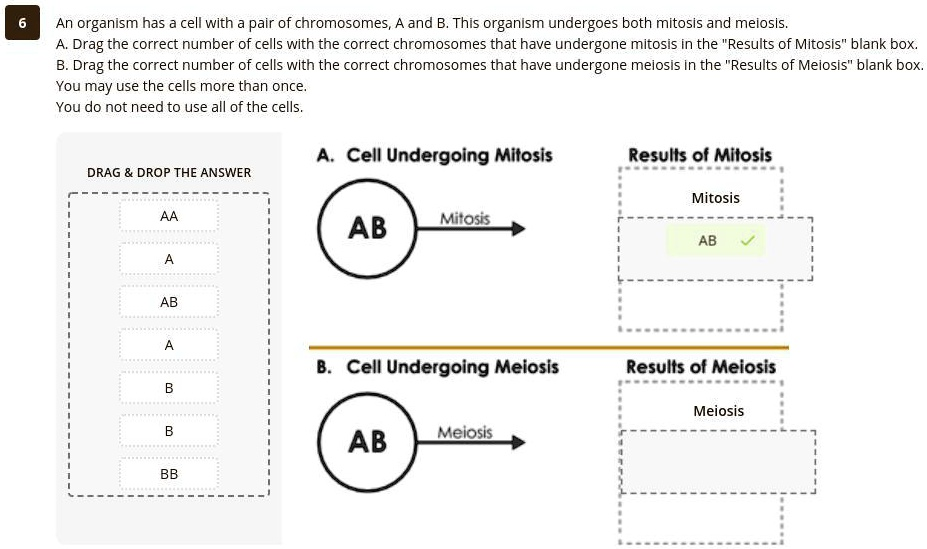
An organism has a cell with a pair of chromosomes, A and B. This organism undergoes both mitosis and meiosis. A. Drag the correct number of cells with the correct chromosomes that have undergone mitosis in the “Results of Mitosis” blank box. B. Drag the correct number of cells with the correct chromosomes that have undergone meiosis in the “Results of Meiosis” blank box. You may use the cells more than once. You do not need to use all of the cells. A. Cell Undergoing Mitosis Results of Mitosis DRAG & DROP THE ANSWER Mitosis AA AB Mitosis AB A AB A B. Cell Undergoing Meiosis Results of Meiosis B Meiosis B AB Meiosis BB
The Correct Answer and Explanation is:
Here is the correct solution for the drag-and-drop activity:
A. Results of Mitosis:
The two blank boxes should both contain a cell with the chromosomes AB.
B. Results of Meiosis:
The four blank boxes should contain two cells with the chromosome A and two cells with the chromosome B.
Explanation
This problem illustrates the fundamental differences between mitosis and meiosis, two types of cell division.
Mitosis
Mitosis is a process of cell division that results in two daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell. It is crucial for growth, tissue repair, and asexual reproduction. The goal of mitosis is to produce exact copies of a cell.
In this scenario, the parent cell is diploid and has a pair of homologous chromosomes, represented as A and B. Before mitosis begins, the cell replicates its DNA. This means chromosome A makes a copy of itself, and so does chromosome B. The cell then undergoes one round of division, where these replicated chromosomes are divided equally between the two new cells. Consequently, each of the two daughter cells receives a full, identical set of chromosomes, one A and one B. Therefore, the result of mitosis is two diploid cells, both with the chromosome combination AB.
Meiosis
Meiosis is a specialized type of cell division that reduces the chromosome number by half, creating four haploid cells (gametes), each genetically distinct from the parent cell and from each other. This process is essential for sexual reproduction.
Meiosis involves two consecutive rounds of division: Meiosis I and Meiosis II. The same parent cell with chromosomes A and B first replicates its DNA. In Meiosis I, the homologous chromosomes (A and B) are separated into two different cells. This is a key difference from mitosis. After Meiosis I, there are two intermediate cells, one containing the replicated A chromosome and the other containing the replicated B chromosome.
In Meiosis II, these two cells divide again. This time, the sister chromatids of each replicated chromosome separate. The cell with the A chromosome divides to produce two cells, each with a single A chromosome. The cell with the B chromosome divides to produce two cells, each with a single B chromosome. The final result of meiosis is four haploid cells: two with chromosome A and two with chromosome B.
