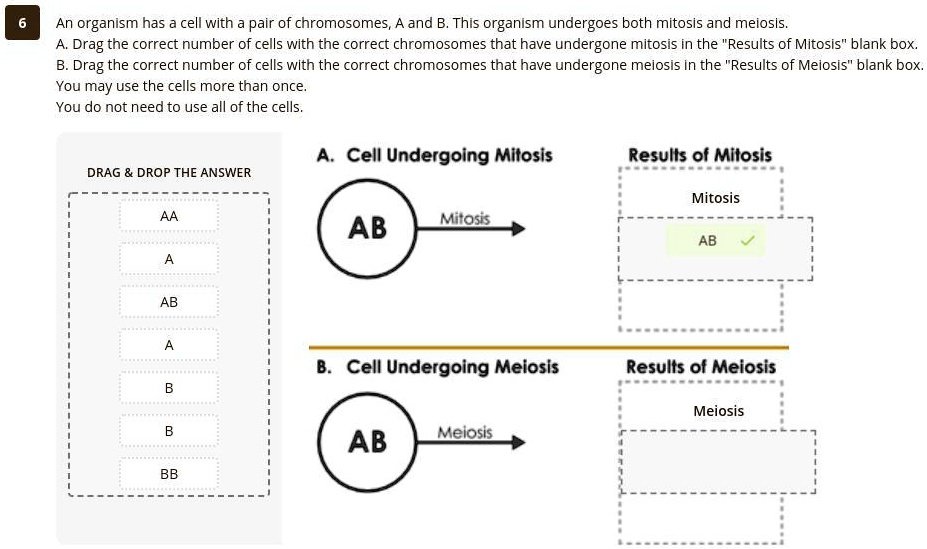
An organism has a cell with a pair of chromosomes, A and B. This organism undergoes both mitosis and meiosis. A. Drag the correct number of cells with the correct chromosomes that have undergone mitosis in the “Results of Mitosis” blank box. B. Drag the correct number of cells with the correct chromosomes that have undergone meiosis in the “Results of Meiosis” blank box. You may use the cells more than once. You do not need to use all of the cells. A. Cell Undergoing Mitosis Results of Mitosis DRAG & DROP THE ANSWER Mitosis AA AB Mitosis AB A AB A B. Cell Undergoing Meiosis Results of Meiosis B Meiosis B AB Meiosis BB
The Correct Answer and Explanation is:
Correct Answer:
A. Results of Mitosis → AB, AB B. Results of Meiosis → A, B
Explanation
Mitosis and meiosis are two distinct processes of cell division that serve different biological purposes. Mitosis is used for growth, repair, and asexual reproduction, producing genetically identical daughter cells. Meiosis, on the other hand, is used for sexual reproduction and results in genetically diverse gametes.
In this case, the organism starts with a diploid cell containing a pair of chromosomes: A and B.
A. Mitosis
During mitosis, the cell duplicates its chromosomes and divides once. The key feature of mitosis is that it maintains the chromosome number. So, a diploid cell (AB) undergoing mitosis will produce two identical diploid daughter cells, each with chromosomes A and B. Therefore, the correct result of mitosis is two cells with AB.
B. Meiosis
Meiosis involves two rounds of division: meiosis I and meiosis II. It starts with a diploid cell (AB) and ends with four haploid cells, each containing one chromosome. The purpose is to reduce the chromosome number by half, producing gametes for sexual reproduction.
In this case, the diploid cell AB undergoes meiosis and produces haploid cells with either chromosome A or chromosome B. The correct result of meiosis is cells with A and B, each representing a haploid gamete. These gametes can later fuse during fertilization to restore the diploid state.
Summary
- Mitosis: AB → AB, AB (two identical diploid cells)
- Meiosis: AB → A, B (haploid gametes)
This distinction is crucial for understanding how organisms grow and reproduce. Mitosis ensures genetic consistency across somatic cells, while meiosis introduces genetic variation and maintains chromosome number across generations.
