Dische diphenylamine test for DNA – Online Procedure: Observing the results Question 14: Based on the color of each tube, which tube do you think contains DNA? Which tube would contain RNA? Which tube would be the negative control with water? Which tube?
The Correct Answer and Explanation is:
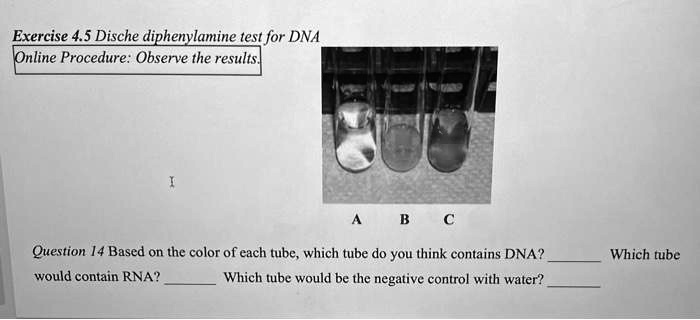
In the Dische diphenylamine test for DNA, the reaction results in color changes that help differentiate DNA from RNA and water, which serve as controls. The colors observed are the key indicators.
Answer:
- Tube containing DNA: Tube A, which would turn blue or deep blue due to the reaction of diphenylamine with the deoxyribose sugar in DNA.
- Tube containing RNA: Tube B, which would turn a faint blue or remain light blue because RNA has ribose and reacts differently to the reagent.
- Negative control with water: Tube C, which would either show no color change or remain clear, indicating the lack of DNA or RNA.
Explanation:
In this experiment, diphenylamine (a reagent) reacts with the sugar backbone of nucleic acids. Specifically, the diphenylamine forms a complex with deoxyribose, a sugar found in DNA, and gives it a characteristic blue color. When the test is conducted on RNA, the color change is less intense because ribose (present in RNA) reacts with the diphenylamine reagent differently. Typically, RNA produces a light blue or no distinct color change in comparison to DNA.
A negative control is essential to ensure that no contamination or false positives occur. Water is used in this case as it lacks nucleic acids. Therefore, when water is tested, it does not react with the diphenylamine reagent, and the tube should remain clear or show no color change.
This test is commonly used to visually distinguish between DNA and RNA based on their reactions to the diphenylamine reagent. The color intensity directly correlates with the presence of deoxyribose (for DNA) or ribose (for RNA), allowing for the determination of nucleic acid type in the sample.
