Perform the Gram-Schmidt process on the following sequence of vectors
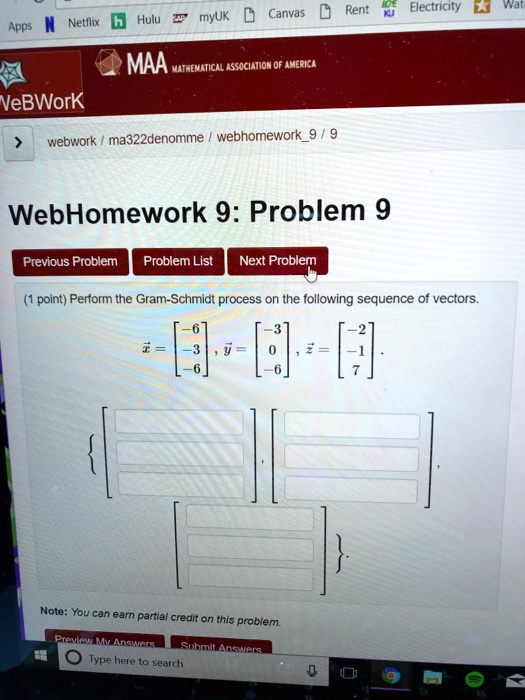
The Correct Answer and Explanation is:
Correct Answer
The orthogonal set of vectors obtained from the Gram-Schmidt process is:
{ [-6, -3, -6], [1, 2, -2], [-2, 2, 1] }
This corresponds to filling the boxes as:
First vector:
-6
-3
-6
Second vector:
1
2
-2
Third vector:
-2
2
1
Explanation
The Gram-Schmidt process is a standard method in linear algebra used to convert a set of linearly independent vectors into an orthogonal set that spans the same subspace. An orthogonal set is one where every pair of vectors is perpendicular, meaning their dot product is zero. This process is essential because working with orthogonal vectors simplifies many calculations. The method works sequentially, taking each vector from the original set and removing its components that are parallel to the previously generated orthogonal vectors.
Let the original vectors be v₁ = [-6, -3, -6], v₂ = [-3, 0, -6], and v₃ = [-2, -1, 7]. We will find the new orthogonal vectors u₁, u₂, and u₃.
- First Vector: The procedure begins by setting the first vector of our new orthogonal set, u₁, equal to the first vector of the original set, v₁.
u₁ = v₁ = [-6, -3, -6]. - Second Vector: To find the second orthogonal vector, u₂, we take the second original vector, v₂, and subtract its projection onto u₁. The formula is u₂ = v₂ – [(v₂ ⋅ u₁) / (u₁ ⋅ u₁)] * u₁.
First, we compute the necessary dot products:
v₂ ⋅ u₁ = (-3)(-6) + (0)(-3) + (-6)(-6) = 18 + 0 + 36 = 54.
u₁ ⋅ u₁ = (-6)² + (-3)² + (-6)² = 36 + 9 + 36 = 81.
The projection coefficient is 54/81, which simplifies to 2/3.
So, u₂ = [-3, 0, -6] – (2/3) * [-6, -3, -6] = [1, 2, -2]. - Third Vector: For the third orthogonal vector, u₃, we take the third original vector, v₃, and subtract its projections onto both u₁ and u₂. The formula is u₃ = v₃ – [(v₃ ⋅ u₁) / (u₁ ⋅ u₁)] * u₁ – [(v₃ ⋅ u₂) / (u₂ ⋅ u₂)] * u₂.
We calculate the new dot products:
v₃ ⋅ u₁ = (-2)(-6) + (-1)(-3) + (7)(-6) = -27.
v₃ ⋅ u₂ = (-2)(1) + (-1)(2) + (7)(-2) = -18.
u₂ ⋅ u₂ = 1² + 2² + (-2)² = 9.
The projection coefficients are -27/81 = -1/3 and -18/9 = -2.
The calculation is u₃ = [-2, -1, 7] – (-1/3) * [-6, -3, -6] – (-2) * [1, 2, -2], which simplifies to u₃ = [-2, 2, 1].
The final set of orthogonal vectors is {[-6, -3, -6], [1, 2, -2], [-2, 2, 1]}.
