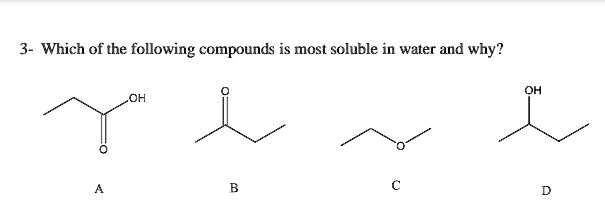
Which of the following compounds is most soluble in water and why? OH
The Correct Answer and Explanation is:
The correct answer is A.
The solubility of a compound in water is determined by the principle of “like dissolves like.” Water is a highly polar, protic solvent, meaning it readily forms hydrogen bonds with itself. Therefore, compounds that are also polar and can participate in extensive hydrogen bonding will be the most soluble in water. The solubility is also influenced by the size of the nonpolar (hydrocarbon) portion of the molecule; a larger nonpolar section decreases water solubility.
Let’s evaluate the four compounds:
- Compound B (butan-2-one) and Compound C (diethyl ether) can only act as hydrogen bond acceptors through the lone pairs on their oxygen atoms. They cannot donate hydrogen bonds, which limits their interaction with water compared to compounds with hydroxyl (OH) groups.
- Compound D (butan-2-ol) is an alcohol. Its hydroxyl group can both donate a hydrogen bond (from the H on the O) and accept hydrogen bonds (at the O). This makes it significantly more soluble than the ketone and ether of a similar size.
- Compound A (propanoic acid) is a carboxylic acid. This compound is the most soluble for several reasons. First, its carboxylic acid functional group (COOH) has two oxygen atoms, providing more sites for hydrogen bonding with water compared to the single oxygen in the alcohol. The hydroxyl group can donate and accept hydrogen bonds, while the carbonyl oxygen can also accept a hydrogen bond. Second, compound A has a smaller nonpolar hydrocarbon chain (three carbons) than compounds B, C, and D (all four carbons), which further increases its solubility.
Most importantly, carboxylic acids are acidic enough to partially ionize in water, donating a proton to form a carboxylate anion (CH₃CH₂COO⁻) and a hydronium ion (H₃O⁺). This formation of ions allows for very strong ion-dipole interactions with polar water molecules, a much stronger force than hydrogen bonding alone. This property dramatically increases the solubility of short-chain carboxylic acids in water, making propanoic acid the most soluble compound among the choices.
