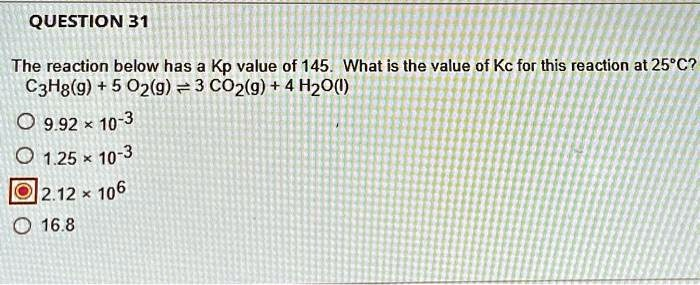
The Correct Answer and Explanation is:
The correct answer is 2.12 x 10⁶.
To find the value of the equilibrium constant in terms of concentration (Kc) from the given equilibrium constant in terms of partial pressure (Kp), we utilize the following standard formula which connects the two constants:
Kp = Kc(RT)^Δn
Let’s break down each part of this equation and determine the values needed for the calculation.
- Identify Known Values:
- Kp = 145 (given)
- T = 25°C. For gas law calculations, temperature must be in Kelvin. T(K) = T(°C) + 273.15. So, T = 25 + 273.15 = 298.15 K.
- R is the ideal gas constant. The appropriate value to use here is 0.08206 L·atm/(mol·K).
- Calculate the Change in Moles of Gas (Δn):
The term Δn represents the change in the number of moles of gas from the reactant side to the product side of the reaction. It is calculated as:
Δn = (total moles of gaseous products) – (total moles of gaseous reactants)Let’s examine the balanced chemical equation:
C₃H₈(g) + 5 O₂(g) ⇌ 3 CO₂(g) + 4 H₂O(l)It is very important to only count the moles of substances in the gaseous state (g). In this reaction, the water (H₂O) is a liquid (l), so it is not included in the calculation for Δn.- Moles of gaseous products = moles of CO₂(g) = 3 mol
- Moles of gaseous reactants = moles of C₃H₈(g) + moles of O₂(g) = 1 mol + 5 mol = 6 mol
Δn = 3 – 6 = -3 - Solve for Kc:
We need to rearrange the original formula to solve for Kc:
Kc = Kp / (RT)^ΔnNow, we can substitute all the known values into this rearranged equation:
Kc = 145 / ( (0.08206) * (298.15) )⁻³
Kc = 145 / (24.466)⁻³Calculating the value inside the parenthesis raised to the power of -3:
(24.466)⁻³ ≈ 6.82 x 10⁻⁵Finally, divide Kp by this value to find Kc:
Kc = 145 / (6.82 x 10⁻⁵)
Kc ≈ 2,125,000When expressed in scientific notation and rounded to three significant figures, the result is:
Kc ≈ 2.12 x 10⁶
This value corresponds to the third answer choice.
