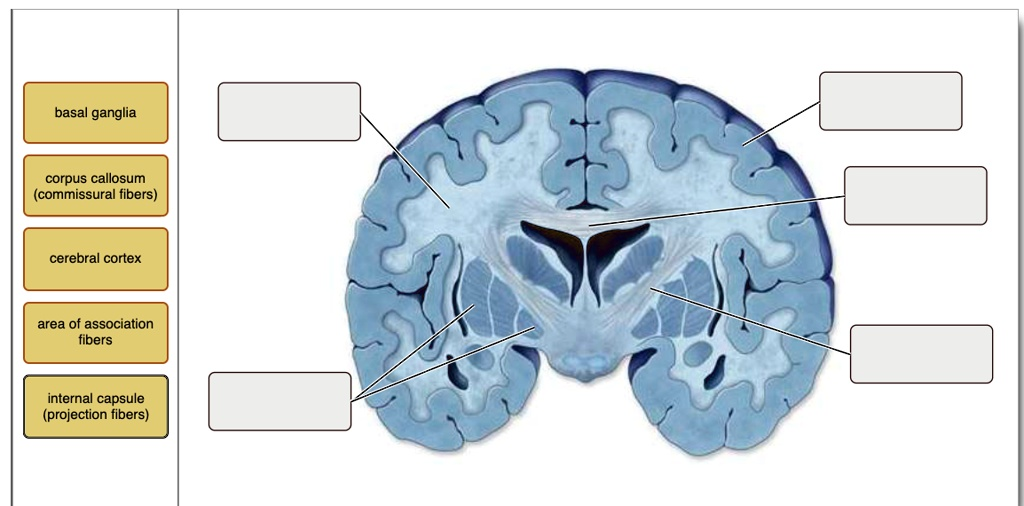
Basal ganglia corpus callosum (commissural fibers) cerebral cortex area of association fibers internal capsule (projection fibers)
The Correct Answer and Explanation is:
Here are the correct labels for the brain structures in the image from top to bottom, matching the provided terms:
- Top right: Cerebral cortex
- Second from top right: Corpus callosum (commissural fibers)
- Third from top right (center of brain): Basal ganglia
- Bottom right: Internal capsule (projection fibers)
- Left middle: Area of association fibers
Explanation
The brain is a complex structure with various regions that perform specific functions and are interconnected through different types of nerve fibers.
- Cerebral cortex: This is the outermost layer of the brain composed of gray matter. It is involved in higher-order brain functions such as thought, perception, voluntary motor control, and decision-making. In the image, it appears as the darkened folded outer layer and is the topmost labeled structure.
- Corpus callosum (commissural fibers): This thick band of nerve fibers connects the left and right hemispheres of the brain, allowing for communication between both sides. Commissural fibers specifically run from one hemisphere to the other. In the image, the corpus callosum is the white curved structure just beneath the cortex at the midline.
- Basal ganglia: These are clusters of neurons located deep within the cerebral hemispheres. They are crucial in coordinating movement, regulating voluntary motor activities, and are involved in reward processing. The basal ganglia are found near the center of the brain in the image, surrounding the dark central cavities.
- Internal capsule (projection fibers): These are bundles of axons that carry information from the cerebral cortex to other areas of the central nervous system. Projection fibers link the cortex with lower brain centers and the spinal cord. In the image, they appear as a white band running between the basal ganglia and the thalamus.
- Area of association fibers: These fibers connect different regions within the same hemisphere of the brain. They allow communication between lobes and are critical for integrating different types of information. In the image, these are labeled within the left hemisphere, deeper than the cortex but not crossing midline or projecting downward.
Each of these structures plays an essential role in the integration and relay of sensory and motor signals, and together they facilitate cognition, movement, and perception.
