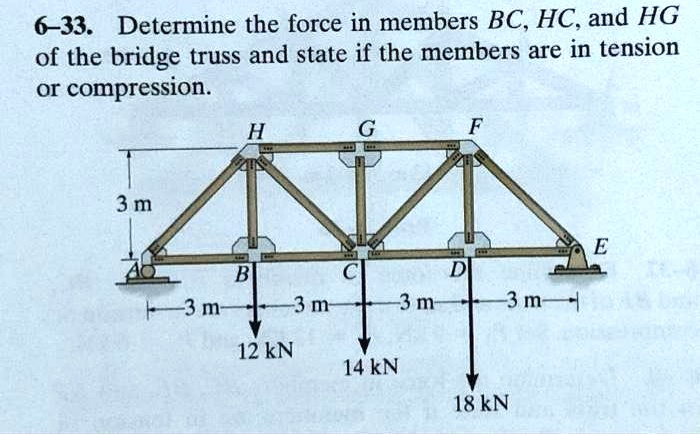
Determine the force in members BC, HC, and HG using the method of sections. State if these members are in tension or compression. 5 kN 4 kN 4 kN 3 kN 2 kN B C D A E 3 m H F + 2 m G 5 m 5 m 5m5m
The Correct Answer and Explanation is:
Here are the final answers and a detailed explanation of the solution.
Final Answer:
- The force in member BC is 20.5 kN in compression.
- The force in member HC is 12.0 kN in tension.
- The force in member HG is 29.0 kN in tension.
Explanation
This problem is solved using the Method of Sections, which allows us to find the forces in specific members without analyzing the entire truss joint by joint.
1. Calculate Support Reactions
First, we must determine the external support reactions at points A and E by treating the entire truss as a rigid body. The support at A is a roller, providing a vertical reaction (Ay). The support at E is a pin, providing both vertical (Ey) and horizontal (Ex) reactions.
- Sum of Horizontal Forces (ΣFx = 0): Since there are no external horizontal loads, the horizontal reaction at E is zero.
- Ex = 0
- Sum of Moments about Point E (ΣME = 0): We sum the moments about pin E to find the reaction at A. We will consider counter-clockwise moments as positive.
- (Ay * 12 m) – (12 kN * 9 m) – (14 kN * 6 m) – (18 kN * 3 m) = 0
- 12Ay – 108 kNm – 84 kNm – 54 kNm = 0
- 12Ay = 246 kNm
- Ay = 20.5 kN
2. Make a Section Cut
To find the forces in members BC, HC, and HG, we make a vertical cut through these three members. This separates the truss into a left and a right section. We will analyze the left section for equilibrium.
3. Analyze the Left Section
We draw a free-body diagram of the left section, which includes joints A, B, and H. The forces acting on this section are the upward reaction Ay (20.5 kN), the downward load at B (12 kN), and the internal forces from the cut members: F_BC, F_HC, and F_HG. We assume all unknown forces are in tension (pulling away from the section).
- Find Force in HG (F_HG): To find F_HG, we sum the moments about point C. This point is chosen because the lines of action for F_BC and F_HC pass through it, so their moments are zero.
- ΣMC = 0
- (20.5 kN * 6 m) – (12 kN * 3 m) – (F_HG * 3 m) = 0
- 123 kNm – 36 kNm = 3*F_HG
- 87 kNm = 3*F_HG
- F_HG = 29.0 kN. The positive result means our assumption of tension was correct.
- Find Force in BC (F_BC): To find F_BC, we can sum moments about point H. The forces F_HG and F_HC pass through H.
- ΣMH = 0
- (20.5 kN * 3 m) + (F_BC * 3 m) = 0
- 61.5 kNm = -3*F_BC
- F_BC = -20.5 kN. The negative sign indicates the force is opposite to our tension assumption, so the member is in compression.
- Find Force in HC (F_HC): We can now find F_HC by summing the vertical forces. The angle of member HC with the vertical is 45 degrees, as the panel height and width are both 3 m.
- ΣFy = 0
- 20.5 kN – 12 kN – F_HC * sin(45°) = 0
- 8.5 kN = F_HC * sin(45°)
- F_HC = 8.5 / sin(45°) = 8.5 / 0.7071
- F_HC = 12.02 kN, which we round to 12.0 kN. The positive result confirms it is in tension.
