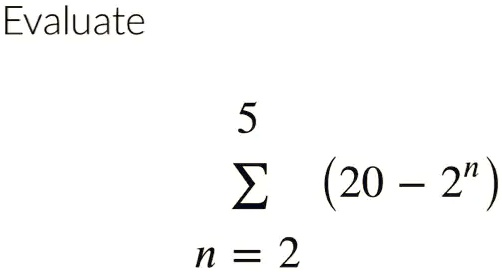
The Correct Answer and Explanation is:
The correct answer is 20.
Explanation
The problem asks to evaluate the summation, represented by the Greek letter sigma (Σ). The expression is the sum of the terms (20 – 2^n) for integer values of n starting from 2 and ending at 5. To solve this, we will substitute each value of n (2, 3, 4, and 5) into the expression, calculate the result for each term, and then add all of these results together.
Let’s break down the calculation for each value of n:
- For n = 2:
The term is (20 – 2²).
2² = 4.
So, the term is (20 – 4) = 16. - For n = 3:
The term is (20 – 2³).
2³ = 8.
So, the term is (20 – 8) = 12. - For n = 4:
The term is (20 – 2⁴).
2⁴ = 16.
So, the term is (20 – 16) = 4. - For n = 5:
The term is (20 – 2⁵).
2⁵ = 32.
So, the term is (20 – 32) = -12.
Now, we sum these four resulting values:
Sum = (Value for n=2) + (Value for n=3) + (Value for n=4) + (Value for n=5)
Sum = 16 + 12 + 4 + (-12)
We can simplify the addition. Notice that we have a +12 and a -12, which cancel each other out:
Sum = 16 + 4 + (12 – 12)
Sum = 16 + 4 + 0
Sum = 20
Alternatively, we could use the properties of summation. The original expression can be split into two separate sums: the sum of 20 and the sum of 2^n. The number of terms is 5 – 2 + 1 = 4.
Sum = Σ(20) – Σ(2^n) from n=2 to 5.
The first part is (4 × 20) = 80.
The second part is (2² + 2³ + 2⁴ + 2⁵) = (4 + 8 + 16 + 32) = 60.
The final result is 80 – 60 = 20. Both methods yield the same answer.
