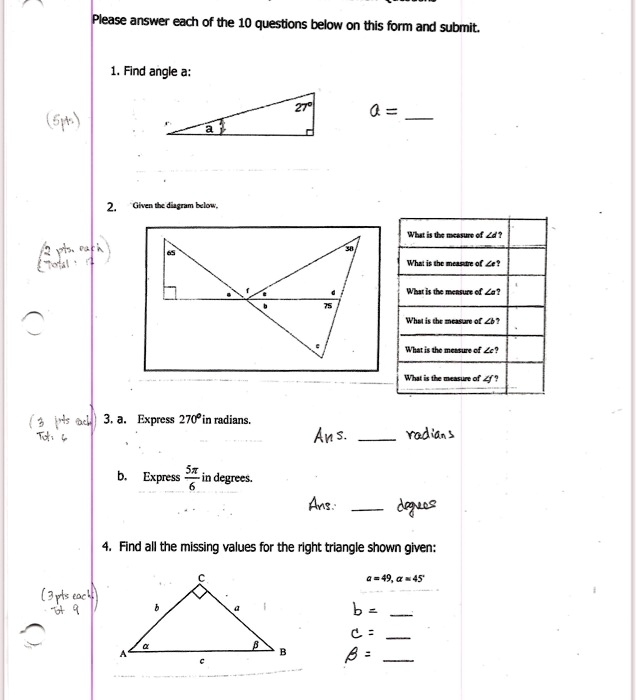
Please answer each of the 10 questions below on this form and submit
The Correct Answer and Explanation is:
Here are the correct answers to the math problems presented in the image, along with a detailed explanation for each solution.
Correct Answers
1. Find angle a:
a = 63°
2. Given the diagram below:
- What is the measure of ∠d? 105°
- What is the measure of ∠e? 90°
- What is the measure of ∠a? 25°
- What is the measure of ∠b? 25°
- What is the measure of ∠c? Undefined (The problem is flawed)
- What is the measure of ∠f? Undefined (The problem is flawed)
3. a. Express 270° in radians:
Ans: (3π/2) radians
3. b. Express 5π/6 in degrees:
Ans: 150 degrees
4. Find all the missing values for the right triangle shown given: a = 49, α = 45°
- b = 49
- c = 49√2 (approximately 69.3)
- β = 45°
Explanation
1. Finding Angle a
The image shows a right-angled triangle. A fundamental rule of geometry is that the sum of the interior angles in any triangle is always 180°. The triangle has one angle of 27°, and the square symbol indicates a right angle, which is 90°. To find angle ‘a’, we subtract the two known angles from 180°.
Calculation: a = 180° – 90° – 27° = 63°.
2. Finding the Angles in the Diagram
This problem requires interpreting a complex diagram. Assuming the numbers 65, 50, and 75 represent angles in degrees, we can find some of the missing values.
- Angle e: The pointer for ‘e’ indicates the angle with the square symbol, which represents a 90° right angle. Therefore, e = 90°.
- Angle a: Angle ‘a’ is part of the top-left triangle, which has angles of 65° and e=90°. The sum of angles is 180°, so a = 180° – 90° – 65° = 25°.
- Angle b: Angles ‘a’ and ‘b’ are vertically opposite at the intersection point, meaning they are equal. Thus, b = a = 25°.
- Angle d: Angle ‘d’ is in the top-right triangle with angles 50° and ‘b’. The sum must be 180°, so d = 180° – 50° – b = 180° – 50° – 25° = 105°.
- Angles c and f: These angles cannot be determined. The diagram is ambiguous or contains errors. For example, if we assume the triangle containing ‘c’ also contains the angle 75° and the angle ‘d’ (105°), their sum (c + 75° + 105°) would already exceed 180°, which is impossible. The placement of ‘f’ is also undefined.
3. Radian and Degree Conversions
- a. Degrees to Radians: To convert degrees to radians, you multiply by the conversion factor (π / 180°).
Calculation: 270° × (π / 180°) = 270π / 180 = (3 × 90)π / (2 × 90) = 3π/2 radians. - b. Radians to Degrees: To convert radians to degrees, you multiply by (180° / π).
Calculation: (5π/6) × (180° / π) = (5 × 180°) / 6 = 900° / 6 = 150°.
4. Solving the Right Triangle
We are given a right triangle (angle C = 90°) with side a = 49 and angle α = 45°.
- Find angle β: In a right triangle, the two acute angles (α and β) sum to 90°. So, β = 90° – α = 90° – 45° = 45°.
- Find side b: Since angle α = angle β = 45°, the triangle is an isosceles right triangle. This means the sides opposite these equal angles are also equal. Side ‘b’ is opposite β and side ‘a’ is opposite α, so b = a = 49.
- Find side c (the hypotenuse): We can use the Pythagorean theorem (a² + b² = c²).
Calculation: 49² + 49² = c² → 2 × 49² = c² → c = √(2 × 49²) = 49√2.
