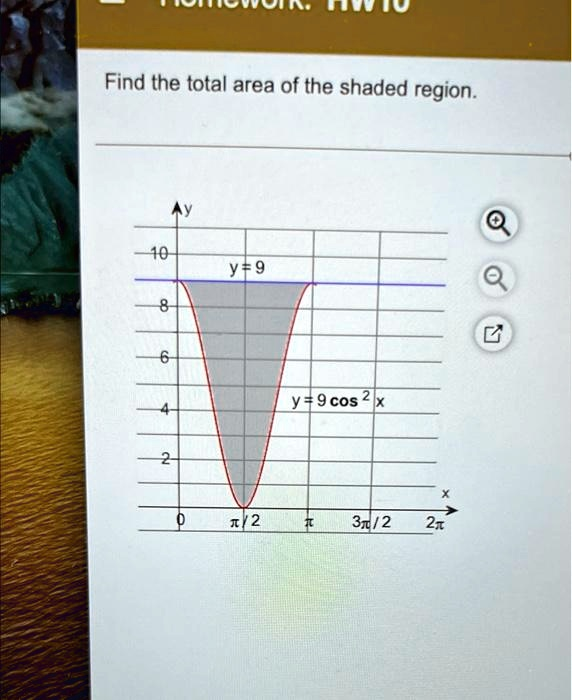
Find the total area of the shaded region. y = 9 y = 9 \cos^2 x
The Correct Answer and Explanation is:
The correct answer is 9π/2.
Explanation
To find the total area of the shaded region, we need to calculate the definite integral of the difference between the upper boundary function and the lower boundary function over the specified interval.
1. Identify the Bounding Functions and Limits of Integration
First, we identify the two functions that enclose the shaded area.
- The upper boundary is the horizontal line given by the equation y = 9.
- The lower boundary is the trigonometric curve given by the equation y = 9 cos²(x).
Next, we determine the limits of integration, which are the x-values where the shaded region begins and ends. These are the points where the two curves intersect. We can find them by setting the two equations equal to each other:
9 = 9 cos²(x)
1 = cos²(x)
Taking the square root of both sides gives:
cos(x) = ±1
From our knowledge of the cosine function, cos(x) = 1 at x = 0, 2π, … and cos(x) = -1 at x = π, 3π, ….
Looking at the provided graph, the shaded region extends from x = 0 to x = π. Therefore, our limits of integration are from a = 0 to b = π.
2. Set Up the Definite Integral
The formula for the area between two curves, f(x) (upper) and g(x) (lower), from x = a to x = b is:
Area = ∫[a, b] (f(x) – g(x)) dx
Substituting our functions and limits:
Area = ∫[0, π] (9 – 9 cos²(x)) dx
3. Solve the Integral
We can simplify the expression by factoring out the constant 9:
Area = 9 ∫[0, π] (1 – cos²(x)) dx
Using the Pythagorean trigonometric identity sin²(x) + cos²(x) = 1, we can replace 1 – cos²(x) with sin²(x):
Area = 9 ∫[0, π] sin²(x) dx
To integrate sin²(x), we use the power-reduction formula: sin²(x) = (1 – cos(2x))/2.
Area = 9 ∫[0, π] (1 – cos(2x))/2 dx
Now, we can integrate:
Area = (9/2) ∫[0, π] (1 – cos(2x)) dx
Area = (9/2) [x – (1/2)sin(2x)] evaluated from 0 to π.
Applying the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus, we evaluate the antiderivative at the upper and lower limits:
Area = (9/2) * [ (π – (1/2)sin(2π)) – (0 – (1/2)sin(0)) ]
Since sin(2π) = 0 and sin(0) = 0, the expression simplifies to:
Area = (9/2) * [ (π – 0) – (0 – 0) ]
Area = (9/2) * π
The total area of the shaded region is 9π/2.
