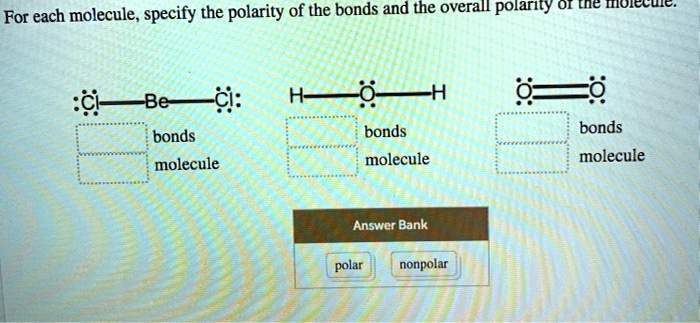
For each molecule, specify the polarity of the bonds and the overall polarity of the liquid. – BeCl2: nonpolar bonds, nonpolar molecule – O2: nonpolar bonds, nonpolar molecule – H2O: polar bonds, polar molecule Answer Bank: – polar – nonpolar
The Correct Answer and Explanation is:
Here are the correct answers for each molecule:
- BeCl₂ (Beryllium chloride)
- Bonds: polar
- Molecule: nonpolar
- H₂O (Water)
- Bonds: polar
- Molecule: polar
- O₂ (Oxygen)
- Bonds: nonpolar
- Molecule: nonpolar
Explanation
The polarity of a chemical bond and an entire molecule are related but distinct concepts. Bond polarity is determined by the difference in electronegativity (ΔEN) between the two atoms forming the bond. Molecular polarity depends on both the polarity of the bonds and the molecule’s three-dimensional geometry.
BeCl₂ (Beryllium chloride): The bond between beryllium (Be) and chlorine (Cl) is polar. Chlorine (electronegativity ≈ 3.16) is significantly more electronegative than beryllium (≈ 1.57), causing electrons to be pulled towards the chlorine atoms. This creates a dipole moment for each Be-Cl bond. However, the overall BeCl₂ molecule is nonpolar. According to VSEPR theory, BeCl₂ has a linear geometry, with the two Cl atoms positioned symmetrically on opposite sides of the central Be atom. The two individual bond dipoles are equal in strength and point in opposite directions, so they cancel each other out, resulting in a net dipole moment of zero for the molecule.
H₂O (Water): The bond between oxygen (O) and hydrogen (H) is polar. Oxygen (electronegativity ≈ 3.44) is much more electronegative than hydrogen (≈ 2.20), creating a strong pull of electrons towards the oxygen atom. This makes the H₂O molecule polar as well. The central oxygen atom has two lone pairs of electrons, which forces the molecule into a bent, asymmetrical shape. Although the image depicts it as linear for simplicity, its true geometry is V-shaped. Because of this bent structure, the two O-H bond dipoles do not cancel each other out. Instead, they combine to create a significant net dipole moment, with a partial negative charge on the oxygen side and partial positive charges on the hydrogen side.
O₂ (Oxygen): The O₂ molecule consists of two identical oxygen atoms. Because the atoms are the same, there is no difference in electronegativity (ΔEN = 0). The electrons in the double bond are shared perfectly equally between the two oxygen atoms, making the bond nonpolar. Since the molecule contains only this nonpolar bond, there are no bond dipoles to consider. Consequently, the entire O₂ molecule is nonpolar.
