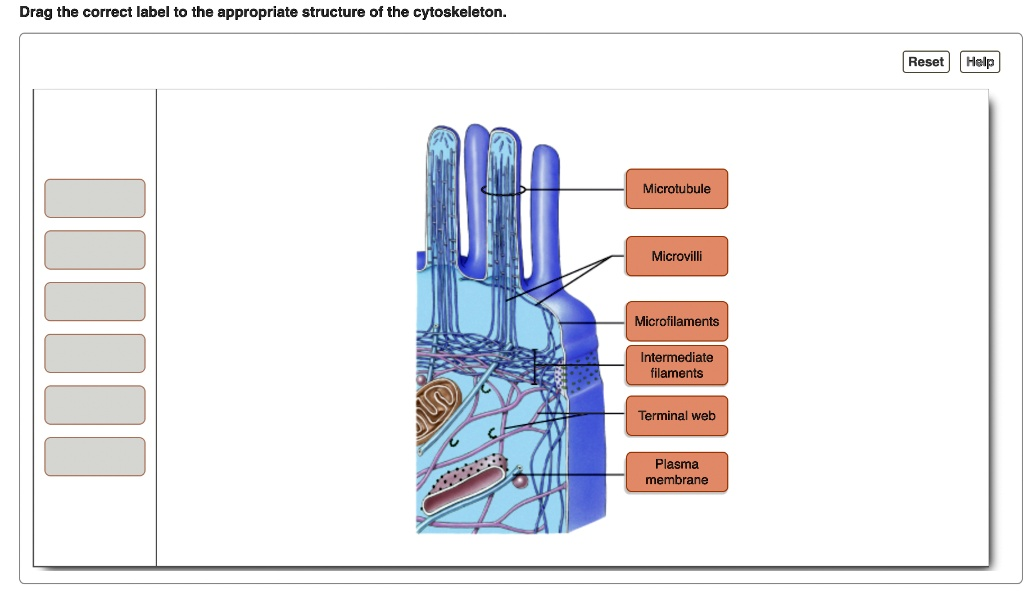
Drag the correct label to the appropriate structure of the cytoskeleton. Microtubule Microvilli Microfilaments Intermediate filaments Terminal web Plasma membrane Reset Help
The Correct Answer and Explanation is:
Here is the correct labeling for the image:
From top to bottom, the labels should be placed in the following order:
- Microtubule
- Microvilli
- Microfilaments
- Intermediate filaments
- Terminal web
- Plasma membrane
Explanation
This diagram illustrates the complex arrangement of the cytoskeleton at the apical surface of a cell, which is the side facing an open space or lumen. Understanding each component is key to appreciating how a cell maintains its shape and function.
The Plasma membrane is the outermost boundary of the animal cell, pointed to by the lowest leader line. This selectively permeable lipid bilayer encloses the entire cell, including the finger-like projections, and regulates the passage of materials into and out of the cytoplasm.
Extending from this surface are the Microvilli. These are the small, finger-like projections that significantly increase the cell’s surface area, which is crucial for cells involved in absorption, such as those lining the small intestine. Each individual projection is a microvillus.
The structural core of each microvillus is composed of Microfilaments. These are the thinnest fibers of the cytoskeleton, made primarily of the protein actin. They provide the rigidity needed to keep the microvilli erect and maintain their shape.
At the base of the microvilli, these microfilaments are anchored into a dense meshwork of filaments called the Terminal web. This structure, located in the apical cytoplasm, acts as a supportive foundation for the microvilli.
The terminal web itself is stabilized by Intermediate filaments. These are cytoskeletal components with a diameter between that of microfilaments and microtubules. They are exceptionally strong, like ropes, and their primary function is to resist mechanical stress and provide tensile strength to the cell, anchoring structures like the terminal web in place.
Deeper within the cytoplasm, we find Microtubules. These are the largest elements of the cytoskeleton, forming hollow tubes composed of the protein tubulin. While not part of the microvilli themselves, microtubules serve as tracks for intracellular transport of organelles and vesicles and play a critical role in maintaining overall cell shape and structure.
