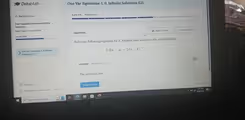
The Correct Answer and Explanation is:
The correct answer to the equation is All Real Numbers, which indicates that there are an infinite number of solutions.
The problem presented is the equation 3(2x + 4) = 2(3x + 6). To find the solution, we must first simplify both sides of the equation by applying the distributive property.
On the left side, we multiply the 3 by each term inside the parentheses. This gives us (3 * 2x) + (3 * 4), which simplifies to 6x + 12.
On the right side, we perform the same operation, multiplying the 2 by each term inside its corresponding parentheses. This results in (2 * 3x) + (2 * 6), which also simplifies to 6x + 12.
After distributing, our new equation is 6x + 12 = 6x + 12. At this point, we can immediately see that both sides of the equation are identical. This type of equation is known as an identity. An identity is an equation that is true for any value substituted for its variable.
To formally complete the solving process, we would attempt to isolate the variable x. We can do this by subtracting 6x from both sides of the equation. When we do this, the variable terms cancel each other out completely: 6x – 6x + 12 = 6x – 6x + 12. This leaves us with the statement 12 = 12.
This resulting statement, 12 = 12, is fundamentally true and does not depend on the value of x. Because the variable has been eliminated and the resulting statement is true, it confirms that any real number we choose for x will satisfy the original equation. Therefore, the equation does not have a single numerical solution but rather an infinite number of solutions. The correct way to express this is “All Real Numbers”.
