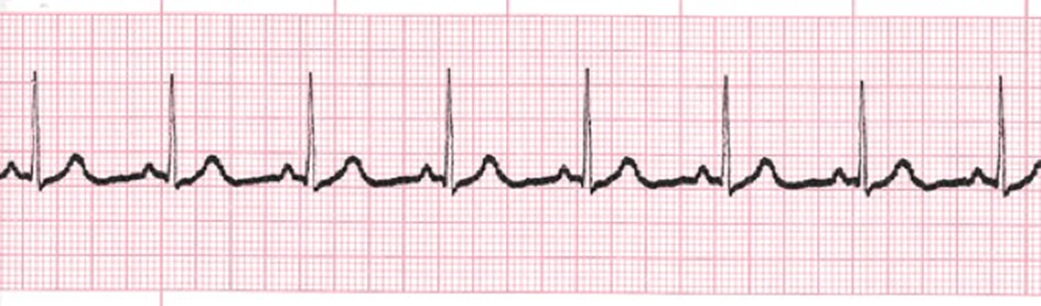
Please identify the following rhythm:
A.
Asystole
B.
Atrial Flutter
C.
Normal Sinus Rhythm
D.
Sinus Bradycardia
To determine the correct rhythm, it’s important to understand each option and its characteristics. Let’s break down each rhythm type:
- Asystole (Option A): Asystole is a state of no cardiac electrical activity, meaning there is no heart rhythm at all. This is characterized by a flatline on the ECG monitor, with no QRS complexes, P waves, or any other cardiac electrical activity visible. It is a critical situation that indicates the absence of effective cardiac output and is a sign of cardiac arrest. Immediate medical intervention is required.
- Atrial Flutter (Option B): Atrial flutter is a type of supraventricular tachycardia where the atria contract rapidly in a regular, repetitive manner. On the ECG, atrial flutter is characterized by a “sawtooth” pattern of P waves known as F-waves, most commonly seen in leads II, III, and aVF. The ventricular rate is often irregular but can be regular depending on the AV node’s conduction ratio.
- Normal Sinus Rhythm (Option C): Normal sinus rhythm (NSR) is the standard rhythm of a healthy heart. It has a regular rate (60-100 beats per minute), with a P wave preceding each QRS complex. The P waves are upright in lead II, and the QRS complexes are narrow and appear regularly. This rhythm indicates a properly functioning heart with normal electrical conduction.
- Sinus Bradycardia (Option D): Sinus bradycardia is a slower-than-normal heart rhythm originating from the sinus node. It is defined as a heart rate less than 60 beats per minute. On the ECG, it has the same characteristics as normal sinus rhythm (P waves before QRS complexes, normal PR interval, and narrow QRS complexes), but with a slower rate.
Correct Answer: Normal Sinus Rhythm (Option C)
Explanation:
Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR) is the rhythm where the electrical impulses originate from the sinus node, which is the heart’s natural pacemaker. It is characterized by the following features:
- Rate: 60-100 beats per minute.
- Rhythm: Regular, with consistent intervals between beats.
- P Waves: Present and appear before each QRS complex, typically upright in lead II.
- PR Interval: Consistent, usually between 0.12 and 0.20 seconds.
- QRS Complexes: Narrow, indicating normal ventricular conduction.
In NSR, each component of the ECG—P waves, QRS complexes, and T waves—appears as expected, reflecting normal heart function. This rhythm signifies that the heart’s electrical system is working properly, and the impulse is traveling through the atria and ventricles in a coordinated manner. It is the ideal rhythm for healthy cardiac function and indicates no immediate issues with heart rate or rhythm.