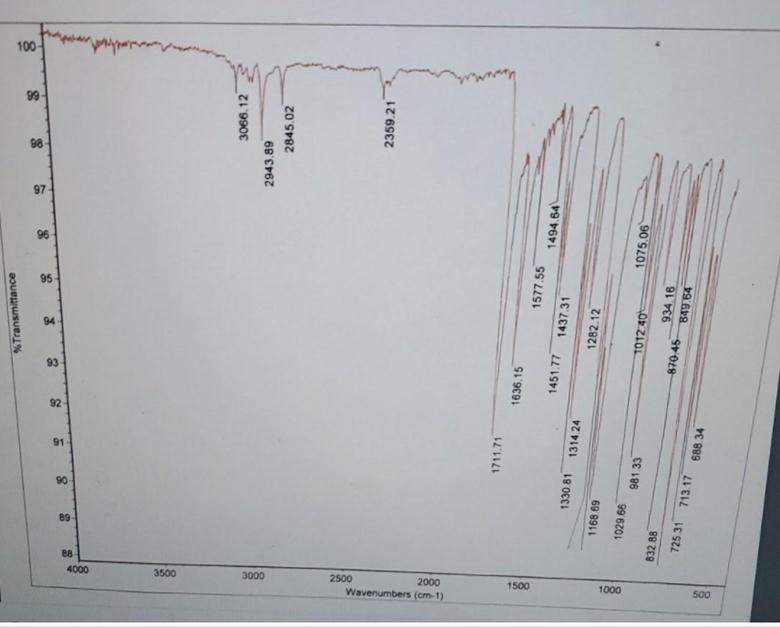
This is an IR spectrum of a sample of methyl cinnamate. In what way do you expect the IR of the product (methyl cinnamate) to be different than the methanol and cinnamic acid that was started with? Based of the IR shown, Is there ar OH stretch? Is there a C=0 stretch? Where should the C=O stretch for this ester (methyl cinnamate) appear?
A rainbow is a result of:
a. different color droplets of water.
b. dispersion.
c. interference.
d. the Huygens Effect.
e. thermal radiation of droplets of water.
a) b) d)
The Correct Answer and Explanation is :
Infrared (IR) spectroscopy is a powerful tool for identifying functional groups in organic compounds by analyzing the absorption of infrared light, which causes molecular vibrations at characteristic frequencies.
Comparison of IR Spectra:
- Methanol (CH₃OH): Exhibits a broad O–H stretching absorption between 3200–3600 cm⁻¹ due to hydrogen bonding, and a C–O stretching absorption around 1000–1100 cm⁻¹.
- Cinnamic Acid (C₆H₅CH=CHCOOH): Shows a broad O–H stretch from the carboxylic acid group around 2500–3000 cm⁻¹, a sharp C=O stretch near 1700 cm⁻¹, and C–O stretching between 1200–1300 cm⁻¹.
- Methyl Cinnamate (C₆H₅CH=CHCOOCH₃): As an ester, it lacks the O–H group, so no broad O–H stretch is present. The ester C=O stretch appears prominently around 1735–1750 cm⁻¹, and the C–O stretch is observed near 1050–1300 cm⁻¹.
Analysis of the Provided IR Spectrum:
- O–H Stretch: The absence of a broad absorption between 3200–3600 cm⁻¹ indicates that there is no O–H stretch, confirming the lack of hydroxyl or carboxylic acid groups in the sample.
- C=O Stretch: A strong absorption band around 1735–1750 cm⁻¹ is characteristic of the ester carbonyl group, confirming the presence of the ester functional group in methyl cinnamate.
Conclusion:
The IR spectrum of methyl cinnamate differs from those of methanol and cinnamic acid by the absence of O–H stretching absorptions and the presence of a strong ester C=O stretch around 1735–1750 cm⁻¹. These spectral features confirm the successful formation of the ester product.
Regarding the Rainbow Phenomenon:
A rainbow is a meteorological phenomenon resulting from the interaction of light with water droplets in the atmosphere. The correct explanation involves:
- Dispersion: Light is refracted upon entering a water droplet, causing different wavelengths (colors) to spread out due to varying refractive indices.
- Refraction: The bending of light as it passes from one medium to another with a different density.
- Reflection: Light reflects off the inner surface of the water droplet.
- Second Refraction: Light refracts again as it exits the droplet, further separating the colors.
This combination of dispersion, refraction, and reflection leads to the formation of a circular arc of colors, commonly observed as a rainbow.
Answer: b. dispersion.