Moment generating function for binomial distribution Let X have the binomial distribution with probability distribution
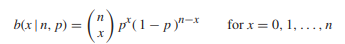
Show that
(a) M(t) = ( 1 − p + pet ) n for all t
(b) E(X) = np and Var(X) = np ( 1 − p )
The Correct Answer and Explanation is :
Let ( X ) be a random variable following a binomial distribution, i.e., ( X \sim \text{Binomial}(n, p) ), where ( n ) is the number of trials and ( p ) is the probability of success in each trial. The probability mass function (PMF) for ( X ) is given by:
[
P(X = k) = \binom{n}{k} p^k (1-p)^{n-k}, \quad k = 0, 1, 2, \dots, n
]
Part (a): Moment Generating Function (MGF)
The moment generating function (MGF) of a random variable ( X ) is defined as:
[
M_X(t) = E(e^{tX}) = \sum_{k=0}^{n} e^{tk} \cdot P(X=k)
]
Substituting the PMF of ( X ), we get:
[
M_X(t) = \sum_{k=0}^{n} e^{tk} \binom{n}{k} p^k (1-p)^{n-k}
]
Factor out terms that do not depend on ( k ):
[
M_X(t) = \left( \sum_{k=0}^{n} \binom{n}{k} p^k (1-p)^{n-k} e^{tk} \right)
]
Recognize that the expression inside the summation is a binomial expansion of ( (p + (1-p)e^t)^n ):
[
M_X(t) = (p + (1-p)e^t)^n
]
Thus, the moment generating function of ( X ) is:
[
M_X(t) = (1 – p + pe^t)^n
]
This confirms part (a).
Part (b): Mean and Variance of ( X )
To compute the mean and variance of ( X ), we use the properties of the MGF. First, recall that:
- The mean is given by ( E(X) = M_X'(0) ).
- The variance is given by ( \text{Var}(X) = M_X”(0) – (M_X'(0))^2 ).
- Mean ( E(X) ):
Differentiate ( M_X(t) ) with respect to ( t ):
[
M_X'(t) = n(1 – p + pe^t)^{n-1} \cdot p e^t
]
Evaluate at ( t = 0 ):
[
M_X'(0) = n(1 – p + p)^{n-1} \cdot p = np
]
Thus, ( E(X) = np ).
- Variance ( \text{Var}(X) ):
Differentiate ( M_X'(t) ) to obtain the second derivative:
[
M_X”(t) = n(n-1)(1 – p + pe^t)^{n-2} \cdot p^2 e^{2t} + n(1 – p + pe^t)^{n-1} \cdot p e^t
]
Evaluate at ( t = 0 ):
[
M_X”(0) = n(n-1)(1 – p + p)^{n-2} \cdot p^2 + n(1 – p + p)^{n-1} \cdot p
]
This simplifies to:
[
M_X”(0) = n(n-1) p^2 + np
]
Now, compute the variance:
[
\text{Var}(X) = M_X”(0) – (M_X'(0))^2 = n(n-1) p^2 + np – (np)^2 = np(1 – p)
]
Thus, the variance of ( X ) is ( \text{Var}(X) = np(1 – p) ).
Conclusion
We have shown that for a binomial random variable ( X ) with parameters ( n ) and ( p ):
- The moment generating function is ( M_X(t) = (1 – p + pe^t)^n ).
- The mean is ( E(X) = np ), and the variance is ( \text{Var}(X) = np(1 – p) ).