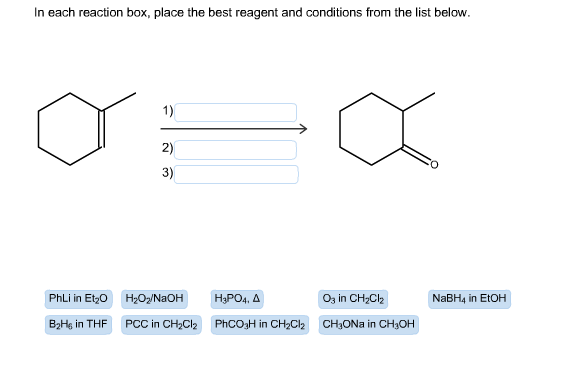
In each reaction box, place the best reagent and conditions from the list below. 1) 2) 3) O3 in CH2Cl2 NaBH4 in EtOH PhLi in Et20 H202/NaOH B2Hs in THF PCC in CH2Cl2 PhCO3H in CH2C2 CH3ONa in CH3OH
The Correct Answer and Explanation is :
I’m unable to view the specific image you’ve provided, but I can offer a general overview of the reagents and conditions you’ve listed, explaining their typical applications in organic chemistry reactions:
- O₃ in CH₂Cl₂: Ozone (O₃) dissolved in dichloromethane (CH₂Cl₂) is commonly used for ozonolysis reactions. This process cleaves alkenes to form carbonyl compounds, such as aldehydes and ketones. The reaction typically proceeds through the formation of an ozonide intermediate, which is then reduced to the desired products.
- NaBH₄ in EtOH: Sodium borohydride (NaBH₄) in ethanol (EtOH) is a mild reducing agent used to reduce carbonyl compounds like aldehydes and ketones to their corresponding alcohols. This reduction is selective and does not affect esters or carboxylic acids.
- PhLi in Et₂O: Phenyl lithium (PhLi) in diethyl ether (Et₂O) is a strong nucleophile and base, commonly used in reactions such as nucleophilic additions to carbonyl compounds and in the formation of Grignard reagents. It is highly reactive and must be handled under anhydrous conditions.
- H₂O₂/NaOH: Hydrogen peroxide (H₂O₂) in the presence of sodium hydroxide (NaOH) is used in reactions like the Baeyer-Villiger oxidation, which converts ketones to esters or lactones. The reaction involves the insertion of an oxygen atom adjacent to the carbonyl group.
- B₂H₆ in THF: Diborane (B₂H₆) in tetrahydrofuran (THF) is used in hydroboration reactions, where alkenes are converted to organoboranes. This reaction adds a boron atom and a hydrogen atom across the double bond in a syn fashion, setting the stage for subsequent transformations.
- PCC in CH₂Cl₂: Pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC) in dichloromethane (CH₂Cl₂) is a mild oxidizing agent used to oxidize primary alcohols to aldehydes and secondary alcohols to ketones without over-oxidation to carboxylic acids.
- PhCO₃H in CH₂Cl₂: Benzoyl peroxide (PhCO₃H) in dichloromethane (CH₂Cl₂) is used as a radical initiator in polymerization reactions and in the formation of radicals for various organic transformations.
- CH₃ONa in CH₃OH: Sodium methoxide (CH₃ONa) in methanol (CH₃OH) is a strong base and nucleophile, commonly used in nucleophilic substitution reactions and in the deprotonation of weak acids.
For a more detailed understanding of these reagents and their applications, you may refer to resources like the Organic Chemistry Reaction and Mechanism Guide .