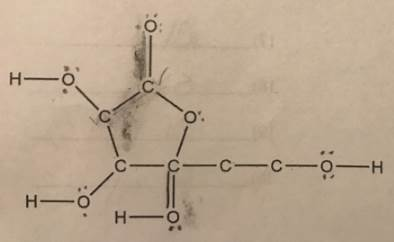
Is formaldehyde polar or nonpolar? The following is an INCOMPLETE Lewis Structure of ascorbic acid (vitamin C) It should have a total of 64 valence electrons, but it’s missing multiple bonds and lone pairs of electrons. Add all of the missing multiple bonds and lone pairs.
The Correct Answer and Explanation is :
Formaldehyde Polarity:
Formaldehyde (CH₂O) is a polar molecule. It has a central carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom and single-bonded to two hydrogen atoms. The molecule is polar due to the following reasons:
- Electronegativity Difference: The oxygen atom is more electronegative than carbon, creating a dipole moment with a partial negative charge on the oxygen and a partial positive charge on the carbon.
- Geometry: The formaldehyde molecule adopts a trigonal planar geometry due to the double bond to oxygen and the two single bonds to hydrogen. This planar structure causes the dipoles from the C=O bond and the C-H bonds to not cancel out, leading to an overall dipole moment.
Thus, formaldehyde is a polar molecule.
Ascorbic Acid Lewis Structure:
I cannot access external links directly, but I can help you with the Lewis structure of ascorbic acid (vitamin C), which has a chemical formula of C₆H₈O₆ and a total of 64 valence electrons.
To properly draw the Lewis structure:
- Valence Electrons:
- Carbon (C) has 4 valence electrons, and there are 6 carbon atoms: ( 6 \times 4 = 24 ).
- Hydrogen (H) has 1 valence electron, and there are 8 hydrogen atoms: ( 8 \times 1 = 8 ).
- Oxygen (O) has 6 valence electrons, and there are 6 oxygen atoms: ( 6 \times 6 = 36 ).
Thus, the total valence electrons = 24 (C) + 8 (H) + 36 (O) = 64 electrons.
- Bonding:
- Start by placing the atoms. Carbon atoms are typically in the center, and oxygen atoms are often double-bonded to carbon or single-bonded with lone pairs.
- Ascorbic acid has both single and double bonds. The hydroxyl (–OH) and carbonyl (C=O) groups must be included.
- Distribute the remaining electrons as lone pairs on oxygen atoms, ensuring that each oxygen gets a full octet.
- Adjusting for Missing Bonds/Lone Pairs:
- After placing the bonds, fill in the missing electrons as lone pairs to ensure the octet rule is followed.
- Multiple bonds might be needed between carbon and oxygen atoms to ensure the correct number of electrons are used.
By following this approach, you should be able to complete the Lewis structure, with the total electrons adding up to 64.
Let me know if you need further clarification!