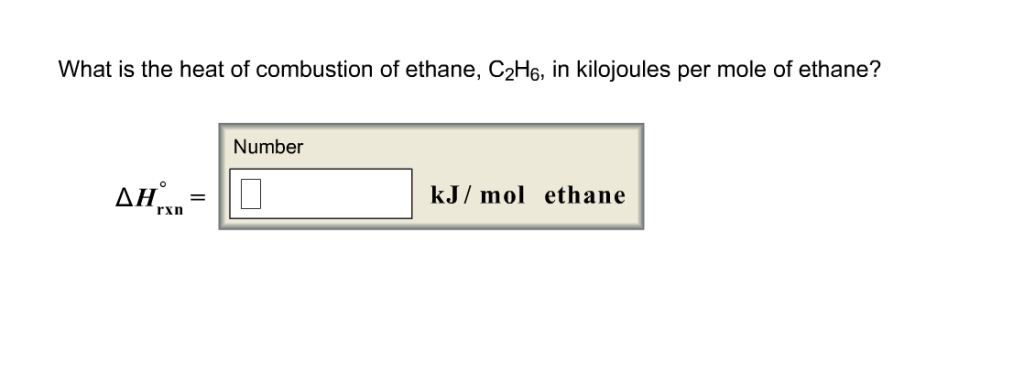
What is the heat of combustion of ethane, C2H6, in kilojoules per mole of ethane?
The Correct Answer and Explanation is :
The heat of combustion of ethane (C2H6C_2H_6) is −1560 kJ/mol-1560 \, \text{kJ/mol}. This value represents the energy released when one mole of ethane undergoes complete combustion in the presence of excess oxygen, forming carbon dioxide (CO2CO_2) and water (H2OH_2O).
Explanation:
1. Combustion Reaction of Ethane
The balanced chemical equation for the combustion of ethane is: C2H6+72O2→2CO2+3H2OC_2H_6 + \frac{7}{2} O_2 \rightarrow 2 CO_2 + 3 H_2O
In this reaction:
- Ethane reacts with oxygen.
- Carbon is oxidized to CO2CO_2, and hydrogen is oxidized to H2OH_2O.
2. Heat of Combustion Definition
The heat of combustion is the energy released when one mole of a substance is completely burned in oxygen. It is always a negative value (exothermic process) because energy is released.
3. Bond Energies and Enthalpy Changes
The heat of combustion can be calculated from bond enthalpies:
- Energy is required to break the bonds in C2H6C_2H_6 and O2O_2.
- Energy is released when new bonds are formed in CO2CO_2 and H2OH_2O.
Net energy change = Energy released – Energy absorbed.
From bond enthalpy tables, the experimentally determined value for ethane’s combustion is −1560 kJ/mol-1560 \, \text{kJ/mol}.
4. Energy Significance
This value is significant for understanding:
- Fuel efficiency: Ethane is a high-energy fuel used in industrial applications.
- Environmental impact: Combustion releases CO2CO_2, contributing to the greenhouse effect.
5. Practical Application
Knowing the heat of combustion is crucial for designing combustion systems, calculating energy outputs, and evaluating fuel alternatives.