Analyze the IR spectrum of Salicylic Acid and manually identify 3 signals in the spectrum that are indicative of the functional groups present in the product.
The Correct Answer and Explanation is :
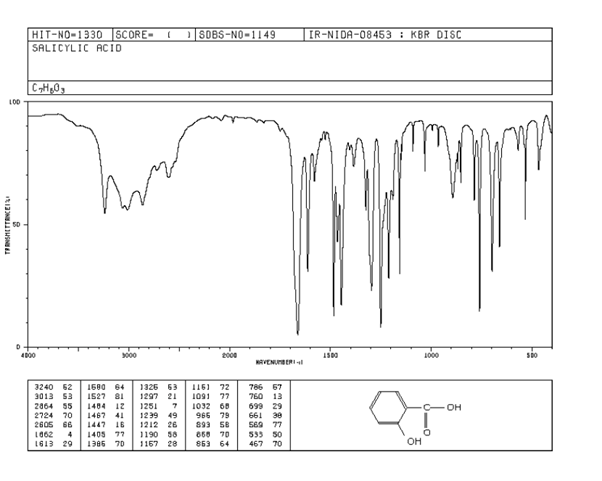
The IR spectrum of salicylic acid can be analyzed to identify key functional groups based on characteristic absorption peaks. Here are three important signals to identify in the spectrum:
- O-H Stretching (Broad Peak)
Location: Around 3200-3600 cm⁻¹
This broad peak corresponds to the hydroxyl (-OH) group of the carboxylic acid and phenolic functional groups. The carboxylic acid O-H stretching typically appears broader due to hydrogen bonding, while the phenol O-H stretching may slightly overlap within this range. - C=O Stretching (Sharp Peak)
Location: Around 1680-1720 cm⁻¹
This sharp and distinct peak is indicative of the carbonyl (C=O) group present in the carboxylic acid. The position of this peak is characteristic of carboxylic acids and helps differentiate it from ketones or aldehydes. - Aromatic C=C Stretching (Medium Intensity)
Location: Around 1500-1600 cm⁻¹
These peaks arise from the aromatic ring stretching vibrations. Salicylic acid contains a benzene ring, and the absorptions in this range confirm the presence of an aromatic structure.
Explanation
Salicylic acid consists of a carboxylic acid group, a hydroxyl group attached to the benzene ring, and an aromatic ring. The IR spectrum serves as a fingerprint to confirm the presence of these functional groups. The broad peak around 3200-3600 cm⁻¹ confirms the hydroxyl group, while the sharp peak near 1700 cm⁻¹ is definitive evidence of the carboxylic acid’s carbonyl group. Additionally, the series of medium-intensity peaks around 1500-1600 cm⁻¹ provides evidence of the aromatic ring.
This analysis validates the structure of salicylic acid, distinguishing it from other compounds by correlating these characteristic peaks with its molecular functional groups.