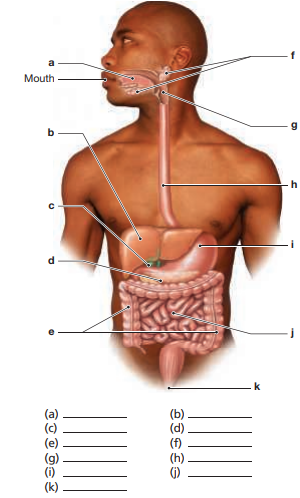
Label the digestive system structures in the following figure.
The Correct Answer and Explanation is :
The digestive system figure shows major structures essential for the digestion and absorption of food. Below is the labeled list of structures and their respective functions:
Labeled Digestive Structures:
- Mouth: The starting point of digestion. Mechanical digestion occurs through chewing, and salivary enzymes (amylase) begin carbohydrate breakdown.
- Esophagus: A muscular tube that transports food from the mouth to the stomach via peristalsis.
- Stomach: A muscular organ where food is mixed with gastric juices containing hydrochloric acid and enzymes (e.g., pepsin) to initiate protein digestion.
- Small Intestine: Divided into three parts:
- Duodenum: First segment where most chemical digestion occurs, aided by bile from the liver and enzymes from the pancreas.
- Jejunum and Ileum: Where nutrient absorption into the bloodstream primarily occurs.
- Large Intestine (Colon): Absorbs water and electrolytes from undigested food, forming solid waste.
- Rectum: Stores feces before they are excreted.
- Anus: The opening through which waste is eliminated.
- Liver: Produces bile, essential for fat digestion and absorption.
- Gallbladder: Stores and concentrates bile, releasing it into the small intestine when needed.
- Pancreas: Produces digestive enzymes (amylase, lipase, protease) and bicarbonate to neutralize stomach acid.
Explanation:
The digestive system is responsible for breaking down food into nutrients that the body can use for energy, growth, and repair. It involves both mechanical digestion (e.g., chewing, churning) and chemical digestion (enzyme activity). Nutrients are absorbed in the small intestine, while the large intestine focuses on water recovery and waste formation. Accessory organs like the liver, pancreas, and gallbladder contribute vital secretions to facilitate digestion.
Efficient coordination of these structures ensures proper nutrient absorption and waste elimination, supporting overall health.