Coordination number: A simple cubic structure is formed when a second layer is laid down directly over the first in a square array. When the structure is extended beyond the unit cell as in the figure above, the coordination number becomes apparent.
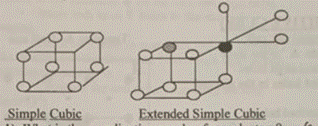
1 What is the coordination number for each atom? 6
2)The structure above is drawn with a large distance between the spheres for clarity. However, the actual packing of atoms in solids is sufficiently close, it can be assumed that the spheres are touching. Where do atoms actually touch in the simple-cubic structure?
a)Along the edge of the cube, b)along the body-diagonal, or c)along the face diagonal?
B) Olong the body din
2 Establish a mathematical relationship between the side of the cube, a, and the radius of the sphere, .
3 What is the number of atoms in the simple-cubic unit cell? setup:
4 What is the volume of all atoms inside the unit cell?
Setup:
5 What is the volume of the cube in terms of ” “?
Setup: .
6 Calculate the percent of unit cell occupied by atoms.
The Correct Answer and Explanation is :
1. Coordination Number
The coordination number of an atom in a simple cubic structure is 6. Each atom in the structure is directly in contact with six nearest neighbors: four in the same plane (one on each side) and one above and one below.
2. Where Do Atoms Touch in a Simple Cubic Structure?
Atoms touch along the edge of the cube in a simple cubic structure. This is because the atoms are arranged such that their centers are aligned along the edges of the unit cell, and their radii meet precisely at those edges.
Correct answer: a) Along the edge of the cube.
3. Mathematical Relationship Between Side Length aa and Sphere Radius rr
In the simple cubic structure:
- Atoms touch along the edge of the cube.
- The side length aa of the cube is equal to twice the radius of the sphere, rr.
a=2ra = 2r
4. Number of Atoms in a Simple Cubic Unit Cell
In the simple cubic structure:
- Each corner atom is shared among 8 unit cells.
- A single unit cell contains 8 corner atoms.
The contribution of each corner atom to a single unit cell is: Contribution per atom=18.\text{Contribution per atom} = \frac{1}{8}.
Thus, the total number of atoms in a simple cubic unit cell is: Number of atoms=8×18=1.\text{Number of atoms} = 8 \times \frac{1}{8} = 1.
5. Volume of All Atoms Inside the Unit Cell
The volume of one sphere is: Vsphere=43πr3.V_{\text{sphere}} = \frac{4}{3} \pi r^3.
Since there is 1 atom per unit cell, the total volume of atoms in the unit cell is: Vatoms=43πr3.V_{\text{atoms}} = \frac{4}{3} \pi r^3.
6. Volume of the Cube in Terms of rr
The side length of the cube is a=2ra = 2r. The volume of the cube is: Vcube=a3=(2r)3=8r3.V_{\text{cube}} = a^3 = (2r)^3 = 8r^3.
7. Percent of Unit Cell Occupied by Atoms
The packing efficiency is calculated as: Packing Efficiency=(Volume of atoms in unit cellVolume of the cube)×100%.\text{Packing Efficiency} = \left(\frac{\text{Volume of atoms in unit cell}}{\text{Volume of the cube}}\right) \times 100\%.
Substitute the values: Packing Efficiency=(43πr38r3)×100%.\text{Packing Efficiency} = \left(\frac{\frac{4}{3} \pi r^3}{8r^3}\right) \times 100\%.
Simplify: Packing Efficiency=(π6)×100%≈52.36%.\text{Packing Efficiency} = \left(\frac{\pi}{6}\right) \times 100\% \approx 52.36\%.
Explanation (300 Words)
In a simple cubic structure, atoms are arranged in a way that they touch along the edges of the cube. The coordination number, which is the number of nearest neighbors surrounding an atom, is 6 in this structure. This relatively low coordination number indicates loose packing compared to other structures like body-centered cubic (BCC) or face-centered cubic (FCC).
The relationship between the cube’s side length (aa) and the radius of the sphere (rr) is a=2ra = 2r. This implies that the atoms just touch each other along the cube’s edges. Each unit cell in this structure contains 1 atom, calculated by considering the fractional contributions of atoms at the corners.
The packing efficiency measures how tightly the atoms are packed within the unit cell. For the simple cubic structure, the packing efficiency is approximately 52.36%, indicating that nearly half the space in the unit cell is empty. This efficiency is derived from the ratio of the volume of the spheres (atoms) to the total volume of the cube. The formula used for packing efficiency is (π/6)×100%(\pi / 6) \times 100\%.
This low packing efficiency explains why simple cubic structures are rare in nature; most materials adopt more efficient packing arrangements like BCC or FCC to minimize empty space and achieve higher densities.