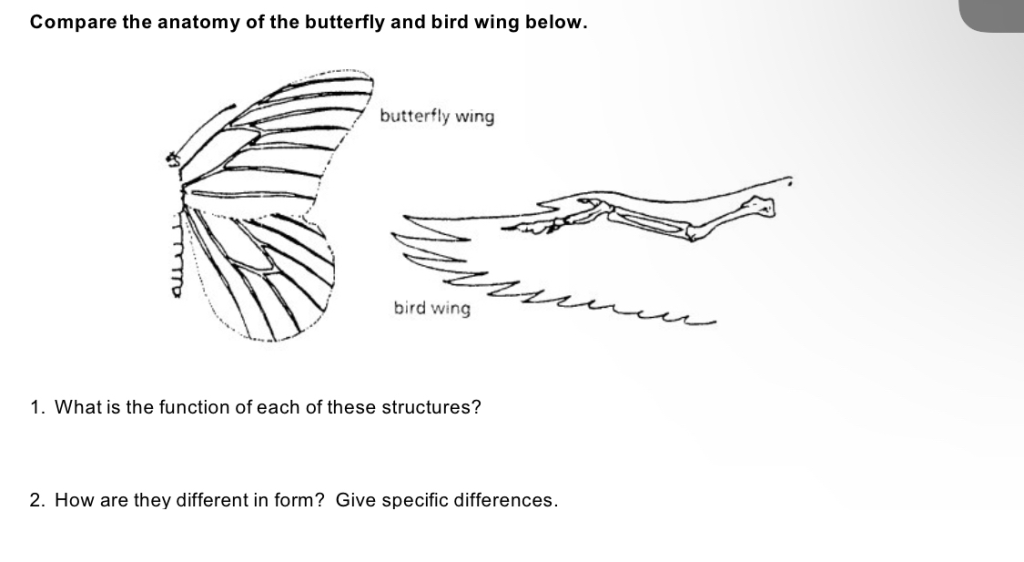
Compare the anatomy of the butterfly and bird wing below.
The Correct Answer and Explanation is :
The anatomy of butterfly and bird wings is a prime example of convergent evolution, where two distinct organisms develop structures serving similar functions. Here’s a comparative analysis:
Differences:
- Structure:
- Butterfly Wings: Composed of chitin, a lightweight and flexible material. The wings are membranous and covered with tiny, overlapping scales that give butterflies their distinctive patterns and colors.
- Bird Wings: Made of bones (humerus, radius, ulna, carpals, and metacarpals) with muscles for movement. They are covered with feathers, which provide lift, maneuverability, and insulation.
- Functionality:
- Butterfly Wings: Primarily used for gliding, thermoregulation, camouflage, and signaling. They lack the musculature to actively flap for sustained flight.
- Bird Wings: Designed for active, powered flight. Muscles attached to the bones allow birds to beat their wings with precision and strength, enabling them to fly over long distances.
- Attachment and Movement:
- Butterfly Wings: Directly attached to the thoracic muscles, which control movement. Their flight relies on up-and-down strokes and is relatively slow.
- Bird Wings: Part of the skeletal system and move via a combination of muscular and skeletal interaction. Birds achieve dynamic flight patterns, including hovering and diving.
- Evolutionary Origin:
- Butterfly Wings: Derived from exoskeletal adaptations in arthropods.
- Bird Wings: Modified forelimbs from vertebrate ancestors.
Explanation:
While both butterfly and bird wings enable flight, their structural differences highlight distinct evolutionary pathways. Butterfly wings, made of chitin, evolved in insects for lightweight gliding, thermoregulation, and signaling. Bird wings, derived from vertebrate forelimbs, consist of bones and feathers, enabling sustained, powered flight. These differences underscore how evolution crafts unique solutions to similar functional demands, emphasizing adaptation to ecological niches rather than shared ancestry.