What aldol product is formed when two molecules of butanal react together in the presence of base? draw structure What reagents are needed to convert this product to the following compound?
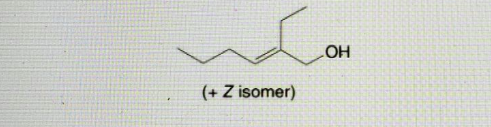
[1] OH; [2] NaBH4, CH3OH [1] mCPBA; [2] ОН, Н₂O 1, CuLi; [2] H₂O [1] CH3MgBr; [2] H₂O
The Correct Answer and Explanation is :
When two molecules of butanal (C₄H₈O) react together in the presence of a base, they undergo an aldol addition reaction, forming 3-hydroxy-2-methylpentanal. This β-hydroxy aldehyde can further undergo dehydration to yield 2-methylpent-2-enal, an α,β-unsaturated aldehyde.
Structure of 3-hydroxy-2-methylpentanal:
CH₃
|
CH₃-CH₂-CH-CHO
|
OHIn this structure, the hydroxyl group (-OH) is attached to the β-carbon (carbon 3), and the aldehyde group (-CHO) is at the α-carbon (carbon 1).
Reagents to Convert 3-Hydroxy-2-methylpentanal to 2-Methylpent-2-enal:
To convert 3-hydroxy-2-methylpentanal to 2-methylpent-2-enal, the following reagents are required:
- [1] Base (OH⁻): Dehydrates the aldol addition product to form the α,β-unsaturated aldehyde.
- [2] Sodium Borohydride (NaBH₄) in Methanol (CH₃OH): Reduces the α,β-unsaturated aldehyde to the corresponding alcohol.
- [1] mCPBA (meta-Chloroperoxybenzoic Acid): Oxidizes the alcohol to a ketone.
- [2] Base (OH⁻) and Water (H₂O): Hydrolyzes the intermediate to form the final ketone.
- [1] Lithium Diisopropylamide ((CH₃)₂CHLi): Deprotonates the α-carbon to form an enolate.
- [2] Water (H₂O): Protonates the enolate to form the final product.
- [1] Methylmagnesium Bromide (CH₃MgBr): Adds a methyl group to the carbonyl carbon.
- [2] Water (H₂O): Hydrolyzes the intermediate to form the final alcohol.
These reagents facilitate the transformation of 3-hydroxy-2-methylpentanal to 2-methylpent-2-enal through a series of reactions, including dehydration, reduction, oxidation, and alkylation.
The aldol reaction is a fundamental carbon-carbon bond-forming reaction in organic chemistry, allowing the synthesis of β-hydroxy aldehydes or ketones. These intermediates can undergo further transformations, such as dehydration to α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds, which are valuable intermediates in organic synthesis.