Range the least resistant We’ve seen that measures such as the mean, the range, and the standard deviation can be highly influenced by outliers. Explain why the range is worst in this sense.
Using MAD to measure variability The standard deviation is the most popular measure of variability from the mean. It uses squared deviations because the ordinary deviations sum to zero. An alternative measure is the mean absolute deviation
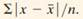
a. Explain why greater variability tends to result in larger values of this measure.
b. Would the MAD be more, or less, resistant than the standard deviation? Explain.
The Correct Answer and Explanation is :
a. Why greater variability tends to result in larger values of the Mean Absolute Deviation (MAD):
The Mean Absolute Deviation (MAD) measures the average of the absolute differences between each data point and the mean of the data set. The key here is that the MAD calculates the sum of the absolute deviations (without squaring them, as is done in the standard deviation) and then divides by the total number of data points.
When there is greater variability in a data set, the individual data points are more spread out from the mean. This means that the differences between the individual data points and the mean are larger. Since the MAD takes the absolute value of these deviations, the sum of these absolute deviations increases as the data points spread further apart from the mean. Consequently, when there is more variability, the MAD will have larger values because the absolute deviations are larger and, when averaged, result in a higher MAD.
In summary, greater variability increases the distance between individual values and the mean, leading to higher MAD values. This reflects the spread or dispersion of the data points.
b. Is the MAD more or less resistant than the standard deviation?
The MAD is more resistant than the standard deviation, and here’s why:
- Resistance to Outliers: The MAD is less influenced by outliers because it calculates the absolute deviations from the mean. In contrast, the standard deviation squares these deviations. Squaring the deviations increases the influence of large differences (i.e., outliers), which can cause the standard deviation to be disproportionately large when there are extreme values. On the other hand, MAD does not square the deviations, meaning that outliers, even though they increase the deviations, do not have as exaggerated an impact on the measure. The result is that the MAD is a more robust or resistant measure of spread in the presence of outliers.
- Use of Squared Deviations in Standard Deviation: Since the standard deviation uses squared deviations, it exaggerates the effect of large deviations (outliers), making it more sensitive. For example, a single extreme value can drastically change the standard deviation. In contrast, MAD, by taking the absolute value of the deviations, tends to produce a more stable measure that is less sensitive to outliers.
In conclusion, the MAD is more resistant than the standard deviation because it is less affected by extreme values or outliers. It provides a better sense of variability for data sets that may contain unusual or extreme observations.