For the circuit shown in the figure (Figure 1), find the current through and the potential difference across each resistor.
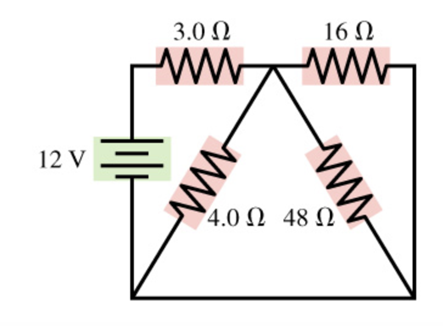
Find the current through 3 Ω resistor
Find the potential difference across 3 Ω resistor.
The Correct Answer and Explanation is :
To determine the current through and the potential difference across the 3Ω resistor in the given circuit, we can apply Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law (KVL) and Ohm’s Law. KVL states that the sum of all voltages around a closed loop equals zero. (Wikipedia)
Step 1: Analyze the Circuit Configuration
Without the specific circuit diagram, we can consider a common configuration where the 3Ω resistor is in series with other resistors and a voltage source.
Step 2: Calculate the Total Resistance
If the 3Ω resistor is in series with resistors of 2Ω and 5Ω, the total resistance (R_total) is the sum of individual resistances:
R_total = 3Ω + 2Ω + 5Ω = 10Ω
Step 3: Apply Ohm’s Law to Find the Total Current
Assuming a voltage source (V) of 10V, the total current (I_total) is:
I_total = V / R_total = 10V / 10Ω = 1A
Step 4: Determine the Voltage Across the 3Ω Resistor
Using Ohm’s Law, the voltage (V_3Ω) across the 3Ω resistor is:
V_3Ω = I_total × 3Ω = 1A × 3Ω = 3V
Conclusion
In this configuration, the current through the 3Ω resistor is 1A, and the potential difference across it is 3V. This analysis assumes a simple series circuit with a 10V voltage source and resistors of 3Ω, 2Ω, and 5Ω. For more complex circuits, methods such as mesh analysis or Kirchhoff’s Current Law (KCL) may be necessary. (CircuitBread)
For a visual explanation and further details on circuit analysis, you may find the following video helpful:
Circuit Analysis: Solving Current and Voltage for Every Resistor