On the weak base/strong and sitration curve bellow, label the following poires a) The point where the pt corresponds to a solution of the weak base (B) in water. b) The point where the pH corresponds to a solution of the conjugate acid (BH) in water. c) The point where pHpK, (for BH”)
The Correct Answer and Explanation is :
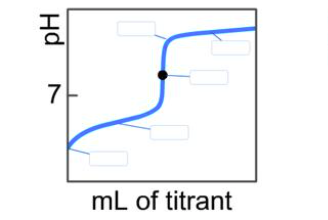
In a titration of a weak base with a strong acid, the pH of the solution changes as the acid is added. The titration curve typically exhibits several key regions:
- Initial pH (before any acid is added): The solution contains only the weak base (B) and water. The weak base partially ionizes in water, producing hydroxide ions (OH⁻) and its conjugate acid (BH⁺). This results in a basic pH, typically above 7.
- Buffer Region: As the strong acid is added, it neutralizes some of the weak base, forming the conjugate acid (BH⁺). This region is characterized by a gradual decrease in pH, as the solution contains a mixture of the weak base and its conjugate acid, acting as a buffer.
- Equivalence Point: At this point, all the weak base has been neutralized by the strong acid, resulting in a solution containing only the conjugate acid (BH⁺) and water. The pH at the equivalence point is typically below 7, indicating an acidic solution.
- Post-Equivalence Region: After the equivalence point, any additional acid added increases the concentration of H⁺ ions, leading to a sharp decrease in pH.
Labeling the Points:
- Point A: This corresponds to the initial pH of the solution, where only the weak base (B) is present in water.
- Point B: This point represents the pH at the equivalence point, where all the weak base has been neutralized, and the solution contains only the conjugate acid (BH⁺) in water.
- Point C: This point corresponds to the pH at the half-equivalence point, where half of the weak base has been neutralized. At this stage, the concentrations of the weak base and its conjugate acid are equal, and the pH equals the pKa of the conjugate acid (BH⁺).
Understanding these points is crucial for interpreting titration curves and determining the pH at various stages of the titration process.