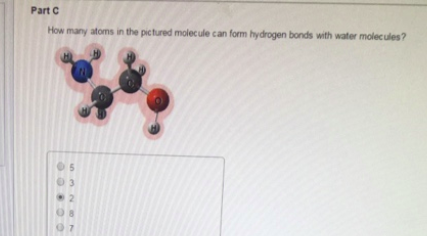
How many atoms in the pictured molecule can form hydrogen bonds with water molecules? 5 3 2 8 7
The Correct Answer and Explanation is :
Hydrogen bonding is a specific type of dipole-dipole interaction that occurs when a hydrogen atom is covalently bonded to a highly electronegative atom—typically nitrogen (N), oxygen (O), or fluorine (F)—and is in close proximity to another electronegative atom with a lone pair of electrons. This interaction is crucial in determining the physical properties of substances, such as the high boiling point of water. (Encyclopedia Britannica)
In the context of a molecule interacting with water, hydrogen bonds can form between the hydrogen atoms of the molecule and the lone pairs of electrons on the oxygen atom of water molecules. The number of such interactions depends on the presence of electronegative atoms in the molecule that can act as hydrogen bond acceptors.
Without access to the specific image of the molecule in question, it’s challenging to provide an exact count of how many atoms in the molecule can form hydrogen bonds with water. However, in general, each hydrogen atom covalently bonded to an electronegative atom (like N, O, or F) can potentially form a hydrogen bond with water. Additionally, lone pairs on electronegative atoms within the molecule can accept hydrogen bonds from water molecules.
For example, in ethanol (CH₃CH₂OH), the hydroxyl group (-OH) can form hydrogen bonds with water molecules through its hydrogen atom and the lone pair on the oxygen atom. Similarly, in ammonia (NH₃), each hydrogen atom can form a hydrogen bond with water molecules, and the lone pair on nitrogen can also accept a hydrogen bond from water. (Chemistry LibreTexts)
In summary, the number of atoms in a molecule that can form hydrogen bonds with water depends on the presence of hydrogen atoms bonded to electronegative atoms and lone pairs on electronegative atoms within the molecule. Each of these can participate in hydrogen bonding interactions with water molecules.