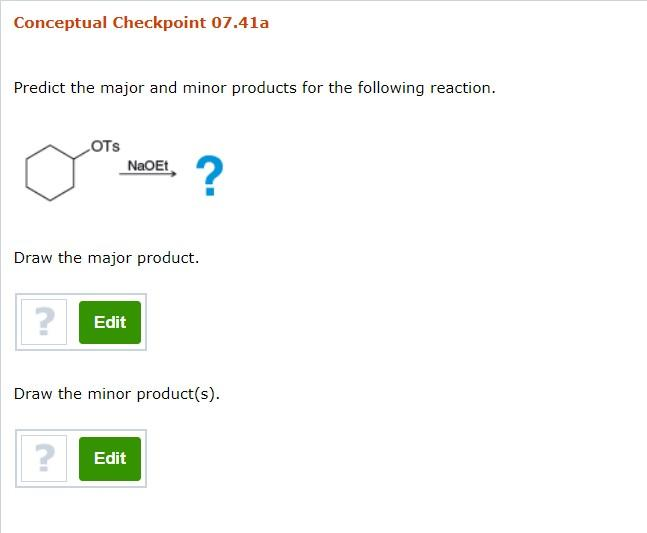
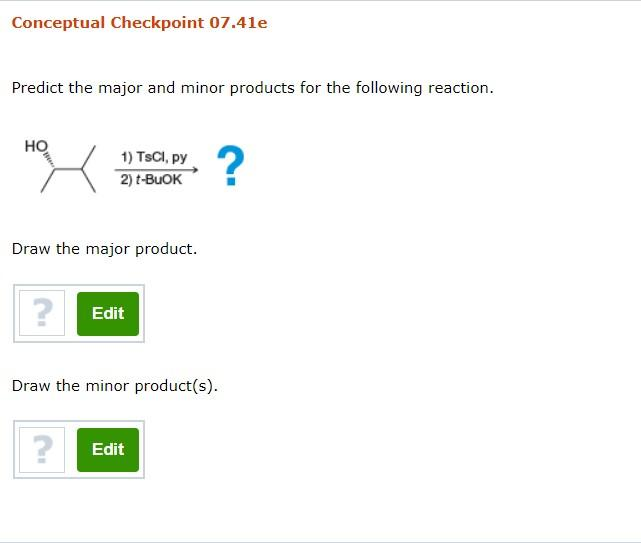
Conceptual Checkpoint 07.41a Predict the major and minor products for the following reaction. OTS NaoEt ? Draw the major product. ? Edit Draw the minor product(s). ? Edit Conceptual Checkpoint 07.410 Predict the major and minor products for the following reaction. OTS NaSH ? Draw the major product. ? Edit Draw the minor product(s). ? Edit No minor products expected. Conceptual Checkpoint 07.41e Predict the major and minor products for the following reaction. HO ht 1) TSCI, py 2) t-BuOK ? Draw the major product. ? Edit Draw the minor product(s). ? Edit Conceptual Checkpoint 07.41f Predict the major and minor products for the following reaction. 1) TsCI, Py OH 2) NaOEt ? Draw the major product. ? Edit Draw the minor product(s). ? Edit
The Correct Answer and Explanation is :
In organic chemistry, predicting the major and minor products of reactions involves understanding the reactivity of functional groups and the influence of reagents and conditions. Let’s analyze the reactions provided:
1. Reaction: OTS + NaOEt
- Reagents: Tosylate (OTs) and sodium ethoxide (NaOEt).
- Mechanism: Sodium ethoxide, a strong nucleophile, will displace the tosyl group via an SN2 mechanism, resulting in the formation of an ether.
- Major Product: The major product is the ether formed by the nucleophilic substitution of the tosyl group with the ethoxide ion.
- Minor Products: No minor products are expected under these conditions.
2. Reaction: OTS + NaSH
- Reagents: Tosylate (OTs) and sodium hydrosulfide (NaSH).
- Mechanism: Sodium hydrosulfide, a strong nucleophile, will displace the tosyl group via an SN2 mechanism, leading to the formation of a thiol.
- Major Product: The major product is the thiol formed by the nucleophilic substitution of the tosyl group with the hydrosulfide ion.
- Minor Products: No minor products are expected under these conditions.
3. Reaction: HO– + TSCI, Py; then t-BuOK
- Reagents: Hydroxide ion (HO–), 2,4,6-triisopropylbenzenesulfonyl chloride (TSCI) in pyridine (Py), followed by tert-butoxide ion (t-BuOK).
- Mechanism:
- Step 1: The hydroxide ion reacts with TSCI in pyridine to form a sulfonate ester, which is a good leaving group.
- Step 2: The tert-butoxide ion, a strong base, abstracts a proton from the β-carbon of the sulfonate ester, leading to an elimination reaction (E2 mechanism) and the formation of an alkene.
- Major Product: The major product is the alkene formed by the E2 elimination of the sulfonate ester.
- Minor Products: No minor products are expected under these conditions.
4. Reaction: TsCl, Py; then NaOEt
- Reagents: Tosyl chloride (TsCl) in pyridine (Py), followed by sodium ethoxide (NaOEt).
- Mechanism:
- Step 1: The hydroxyl group (-OH) reacts with TsCl in pyridine to form a tosylate ester, enhancing the leaving group’s ability.
- Step 2: Sodium ethoxide, a strong nucleophile, displaces the tosyl group via an SN2 mechanism, resulting in the formation of an ether.
- Major Product: The major product is the ether formed by the nucleophilic substitution of the tosyl group with the ethoxide ion.
- Minor Products: No minor products are expected under these conditions.
In summary, each reaction involves a nucleophilic substitution or elimination mechanism, leading to the formation of the major product as indicated. No minor products are expected under the specified conditions.