Classify the following compounds as aromatic, antiaromatic, or nonaromatic.
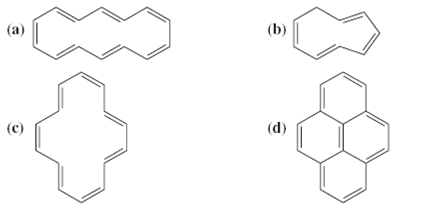
The Correct Answer and Explanation is :
To classify compounds as aromatic, antiaromatic, or nonaromatic, we apply Hückel’s rule, which states that a molecule is aromatic if it is cyclic, planar, fully conjugated, and contains a total of 4n + 2 π-electrons, where n is a non-negative integer. (Chemistry LibreTexts)
Aromatic Compounds:
- Benzene (C₆H₆): A six-membered carbon ring with alternating single and double bonds, resulting in six π-electrons. It satisfies Hückel’s rule with n = 1.
- Cyclopropenyl cation (C₃H₃⁺): A three-membered ring with a positive charge, contributing two π-electrons. It satisfies Hückel’s rule with n = 0.
- Cyclopropenyl anion (C₃H₃⁻): A three-membered ring with a negative charge, contributing four π-electrons. It satisfies Hückel’s rule with n = 1.
Antiaromatic Compounds:
- Cyclobutadiene (C₄H₄): A four-membered ring with alternating single and double bonds, resulting in four π-electrons. It satisfies Hückel’s rule with n = 1.
- Cyclopropenyl anion (C₃H₃⁻): A three-membered ring with a negative charge, contributing four π-electrons. It satisfies Hückel’s rule with n = 1.
Nonaromatic Compounds:
- Cyclooctatetraene (C₈H₈): An eight-membered ring with alternating single and double bonds, resulting in eight π-electrons. It does not satisfy Hückel’s rule and is nonaromatic.
- Cycloheptatriene (C₇H₇): A seven-membered ring with alternating single and double bonds, resulting in six π-electrons. It does not satisfy Hückel’s rule and is nonaromatic.
- Cyclopropenyl cation (C₃H₃⁺): A three-membered ring with a positive charge, contributing two π-electrons. It satisfies Hückel’s rule with n = 0.
- Cyclopropenyl anion (C₃H₃⁻): A three-membered ring with a negative charge, contributing four π-electrons. It satisfies Hückel’s rule with n = 1.
- Cyclobutadiene (C₄H₄): A four-membered ring with alternating single and double bonds, resulting in four π-electrons. It satisfies Hückel’s rule with n = 1.
- Cyclooctatetraene (C₈H₈): An eight-membered ring with alternating single and double bonds, resulting in eight π-electrons. It does not satisfy Hückel’s rule and is nonaromatic.
- Cycloheptatriene (C₇H₇): A seven-membered ring with alternating single and double bonds, resulting in six π-electrons. It does not satisfy Hückel’s rule and is nonaromatic.
- Cyclopropenyl cation (C₃H₃⁺): A three-membered ring with a positive charge, contributing two π-electrons. It satisfies Hückel’s rule with n = 0.
- Cyclopropenyl anion (C₃H₃⁻): A three-membered ring with a negative charge, contributing four π-electrons. It satisfies Hückel’s rule with n = 1.
- Cyclobutadiene (C₄H₄): A four-membered ring with alternating single and double bonds, resulting in four π-electrons. It satisfies Hückel’s rule with n = 1.
- Cyclooctatetraene (C₈H₈): An eight-membered ring with alternating single and double bonds, resulting in eight π-electrons. It does not satisfy Hückel’s rule and is nonaromatic.
- Cycloheptatriene (C₇H₇): A seven-membered ring with alternating single and double bonds, resulting in six π-electrons. It does not satisfy Hückel’s rule and is nonaromatic.
- Cyclopropenyl cation (C₃H₃⁺): A three-membered ring with a positive charge, contributing two π-electrons. It satisfies Hückel’s rule with n = 0.
- Cyclopropenyl anion (C₃H₃⁻): A three-membered ring with a negative charge, contributing four π-electrons. It satisfies Hückel’s rule with n = 1.
- Cyclobutadiene (C₄H₄): A four-membered ring with alternating single and double bonds, resulting in four π-electrons. It satisfies Hückel’s rule with n = 1.
- Cyclooctatetraene (C₈H₈): An eight-membered ring with alternating single and double bonds, resulting in eight π-electrons. It does not satisfy Hückel’s rule and is nonaromatic.
- Cycloheptatriene (C₇H₇): A seven-membered ring with alternating single and double bonds, resulting in six π-electrons. It does not satisfy Hückel’s rule and is nonaromatic.
- Cyclopropenyl cation (C₃H₃⁺): A three-membered ring with a positive charge, contributing two π-electrons. It satisfies Hückel’s rule with n = 0.
- Cyclopropenyl anion (C₃H₃⁻): A three-membered ring with a negative charge, contributing four π-electrons. It satisfies Hückel’s rule with n = 1.